Novel Photocatalytic PVDF/Nano-TiO₂ Hollow Fibers for Environmental Remediation
- PMID: 30961059
- PMCID: PMC6403937
- DOI: 10.3390/polym10101134
Novel Photocatalytic PVDF/Nano-TiO₂ Hollow Fibers for Environmental Remediation
Abstract
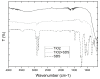
Polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) mixed matrix membranes loaded with inorganic TiO₂ nanoparticles have received increasing attention in the last few years as self-cleaning membranes for possible application in wastewater treatment and seawater filtration. These novel membranes show increased hydrophilicity, stability and catalytic activity under UV-A irradiation. In this work, PVDF-TiO₂ hollow fibers were prepared by employing new strategies for enhancing the stability of the TiO₂ dispersion, reducing particle agglomeration and improving their distribution. The spinning conditions for producing ultrafiltration hollow fiber membranes from PVDF material and nano-TiO₂ were investigated. Finally, the optimized fibers have been characterized and tested for methylene blue (MB) degradation in water and salty seawater, revealing good permeability, long-term stability under UV-A irradiation, and photo-catalytic activity in both test solutions.
Keywords: PVDF; TiO2; hollow fiber membranes; mixed matrix membrane; photocatalytic degradation; ultrafiltration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Pendergast M.M., Hoek E.M.V. A review of water treatment membrane nanotechnologies. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011;4:1946. doi: 10.1039/c0ee00541j. - DOI
-
- Zularisam A.W., Ismail A.F., Salim R. Behaviours of natural organic matter in membrane filtration for surface water treatment—A review. Desalination. 2006;194:211–231. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2005.10.030. - DOI
-
- Drioli E., Stankiewicz A.I., Macedonio F. Membrane engineering in process intensification-An overview. J. Memb. Sci. 2011;380:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2011.06.043. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

