Continuous distraction osteogenesis device with MAAC controller for mandibular reconstruction applications
- PMID: 30961605
- PMCID: PMC6454606
- DOI: 10.1186/s12938-019-0655-0
Continuous distraction osteogenesis device with MAAC controller for mandibular reconstruction applications
Abstract
Background: Distraction osteogenesis (DO) is a novel technique widely used in human body reconstruction. DO has got a significant role in maxillofacial reconstruction applications (MRA); through this method, bone defects and skeletal deformities in various cranio-maxillofacial areas could be reconstructed with superior results in comparison to conventional methods. Recent studies revealed in a DO solution, using an automatic continuous distractor could significantly improve the results while decreasing the existing issues. This study is aimed at designing and developing a novel automatic continuous distraction osteogenesis (ACDO) device to be used in the MRA.
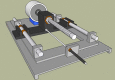
Methods: The design is comprised of a lead screw translation mechanism and a stepper motor, placed outside of the mouth to generate the desired continuous linear force. This externally generated and controlled distraction force (DF) is transferred into the moving bone segment via a flexible miniature transition system. The system is also equipped with an extra-oral ACDO controller, to generate an accurate, reliable, and stable continuous DF.
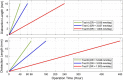
Results: Simulation and experimental results have justified the controller outputs and the desired accuracy of the device. Experiments have been conducted on a sheep jaw bone and results have showed that the developed device could offer a continuous DF of 38 N with distraction accuracy of 7.6 nm on the bone segment, while reducing the distraction time span.
Conclusion: Continuous DF with high resolution positioning control, along with the smaller size of the distractor placed in the oral cavity will help in improving the result of the reconstruction operation and leading to a successful DO procedure in a shorter time period. The developed ACDO device has less than 1% positioning error while generating sufficient DF. These features make this device a suitable distractor for an enhanced DO treatment in MRA.
Keywords: Automatic continuous distractor; Distraction osteogenesis; Medical devices.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures












Similar articles
-
Hybrid Distractor for Continuous Mandibular Distraction Osteogenesis.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Nov 28;9(12):732. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9120732. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36550938 Free PMC article.
-
Review of automatic continuous distraction osteogenesis devices for mandibular reconstruction applications.Biomed Eng Online. 2020 Apr 1;19(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s12938-020-00761-8. Biomed Eng Online. 2020. PMID: 32238159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two-Axis Continuous Distractor for Mandibular Reconstruction.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Aug 6;9(8):371. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9080371. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36004896 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic continuous distraction osteogenesis device for hand reconstruction applications.Med Eng Phys. 2022 Mar;101:103770. doi: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2022.103770. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Med Eng Phys. 2022. PMID: 35232550
-
Automated continuous mandibular distraction osteogenesis: review of the literature.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012 Feb;70(2):407-16. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2011.01.042. Epub 2011 Jun 15. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012. PMID: 21676514 Review.
Cited by
-
Hybrid Distractor for Continuous Mandibular Distraction Osteogenesis.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Nov 28;9(12):732. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9120732. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36550938 Free PMC article.
-
Real-Time Wireless Platform for In Vivo Monitoring of Bone Regeneration.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Aug 15;20(16):4591. doi: 10.3390/s20164591. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32824259 Free PMC article.
-
Review of automatic continuous distraction osteogenesis devices for mandibular reconstruction applications.Biomed Eng Online. 2020 Apr 1;19(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s12938-020-00761-8. Biomed Eng Online. 2020. PMID: 32238159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experimental validation of finite element simulation of a new custom-designed fixation plate to treat mandibular angle fracture.Biomed Eng Online. 2021 Feb 5;20(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12938-021-00851-1. Biomed Eng Online. 2021. PMID: 33546713 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA Methyltransferase METTL3 Promotes Endothelial Progenitor Cell Angiogenesis in Mandibular Distraction Osteogenesis via the PI3K/AKT Pathway.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 1;9:720925. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.720925. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34790657 Free PMC article.
References
-
- El-Ghannam A. Bone reconstruction: from bioceramics to tissue engineering. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2005;2(1):87–101. - PubMed
-
- Perry CR. Bone repair techniques, bone graft, and bone graft substitutes. Clin Orthopaed Relat Res. 1999;360:71–86. - PubMed
-
- Ilizarov GA. The principles of the Ilizarov method. Bull Hosp Joint Dis Orthop Instit. 1987;48(1):1–11. - PubMed
-
- Aykan A, et al. Mandibular distraction osteogenesis with newly designed electromechanical distractor. J Craniofacial Surg. 2014;25(4):1519–1523. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

