Anticalcifying effect of Daucus carota in experimental urolithiasis in Wistar rats
- PMID: 30962051
- PMCID: PMC7527822
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaim.2018.12.003
Anticalcifying effect of Daucus carota in experimental urolithiasis in Wistar rats
Abstract
Background: Urolithiasis is a burgeoning disease that results from pathological biomineralization. Daucus carota L. is a widely consumed food crop with reported nephroprotective and diuretic activity. Its potential for Ashmari bhedan (destruction of stone/calculi) or treatment of urinary calculi has been explored traditionally. However, no scientific evidence is available to prove its antiurolithiatic efficacy. Moreover, establishing the antiurolithiatic effects of D. carota, an extensively consumed commodity with numerous health benefits, would provide a beneficial dietary measure for the prevention and cure of urolithiasis.
Objective: The study aimed at investigating in vivo antiurolithiatic potential of hydroethanolic extract of D. carota roots against calcium oxalate urolithiasis.
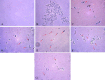
Materials and methods: Ethylene glycol and ammonium chloride induced hyperoxaluria model of urolithiasis in male Wistar rats was used for the study. Urine and serum parameters and, kidney histopathology was used to determine the antilithic efficacy of D. carota root extract.
Results: D. carota extract significantly ameliorated abnormal urinary levels of calcium, oxalate, phosphate, magnesium, citrate, protein and uric acid in lithogenic rats. Serum BUN, creatinine and uric acid levels; and calcium, phosphate and oxalate deposition in kidney tissue were also rendered normal following D. carota treatment. D. carota extract also prevented oxidative stress mediated renal tissue degeneration both prophylactically and curatively.
Conclusion: This study suggests antiurolithiatic effect of D. carota roots, which can be attributed to its anticrystallization property, ability to ameliorate urine and serum biochemistry and renal cellularity.
Keywords: Calcium oxalate; HPLC; Histopathology; Renal stones.
Copyright © 2019 Transdisciplinary University, Bangalore and World Ayurveda Foundation. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Antiurolithiatic effects of Cassia fistula Lin. fruit extracts on ethylene glycol-induced nephrolithiasis in rats.Microsc Res Tech. 2024 Jul;87(7):1494-1506. doi: 10.1002/jemt.24521. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Microsc Res Tech. 2024. PMID: 38415887
-
NEPHROPROTECTIVE AND DIURETIC EFFECT OF NIGELLA SATIVA L SEEDS OIL ON LITHIASIC WISTAR RATS.Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2016 Sep 29;13(6):204-214. doi: 10.21010/ajtcam.v13i6.30. eCollection 2016. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 28480381 Free PMC article.
-
Alteration in Oxidative/nitrosative imbalance, histochemical expression of osteopontin and antiurolithiatic efficacy of Xanthium strumarium (L.) in ethylene glycol induced urolithiasis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Dec;84:1524-1532. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.11.029. Epub 2016 Nov 18. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27876212
-
Antiurolithiatic activity of saponin rich fraction from the fruits of Solanum xanthocarpum Schrad. & Wendl. (Solanaceae) against ethylene glycol induced urolithiasis in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Oct 31;144(1):160-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.08.043. Epub 2012 Sep 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22981722
-
Dietary treatment of urinary risk factors for renal stone formation. A review of CLU Working Group.Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2015 Jul 7;87(2):105-20. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2015.2.105. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2015. PMID: 26150027 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of Ficus tikoua Bur. extract in ethylene glycol-induced urolithiasis model in SD rats.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 29;13:974947. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.974947. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36105205 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Role of Phenolic Compounds in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review.Molecules. 2024 May 30;29(11):2576. doi: 10.3390/molecules29112576. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38893451 Free PMC article.
-
Morin hydrate mitigates calcium oxalate urolithiasis by inhibiting oxalate synthesis and modulating crystal formation.Urolithiasis. 2024 Sep 6;52(1):127. doi: 10.1007/s00240-024-01628-6. Urolithiasis. 2024. PMID: 39237821
References
-
- Alatab S., Pourmand G., El Howairis M.E., Buchholz N., Najafi I., Pourmand M.R. National profiles of urinary calculi a comparison between developing and developed worlds. Iran J Kidney Dis. 2016;10:51–61. - PubMed
-
- Bouatia M., Benramdane L., Idrissi M.O., Draoui M. An epidemiological study on the composition of urinary stones in Morocco in relation to age and sex. Afr J Urol. 2015;21:194–197. doi: 10.1016/j.afju.2015.02.006. - DOI
-
- McKenzie G., Hall J. Management of stone disease. Surgery (Oxford) 2013;31:354–361.
-
- Bawari S., Sah A.N., Tewari D. Urolithiasis: an update on diagnostic modalities and treatment protocols. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2017;79:164–174. doi: 10.4172/pharmaceutical-sciences.1000214. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

