Dental management of patients with haemophilia in the era of recombinant treatments: increased efficacy and decreased clinical risk
- PMID: 30962210
- PMCID: PMC6453434
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2018-227974
Dental management of patients with haemophilia in the era of recombinant treatments: increased efficacy and decreased clinical risk
Abstract
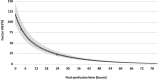
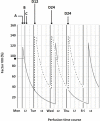
Haemophilia is a hereditary X-linked recessive disorder caused by a deficiency of either clotting factor VIII (haemophilia A) or IX (haemophilia B). Conventional treatment is currently based on the use of either plasma derived or recombinant coagulation factors. This paper reports on the case of a patient with severe haemophilia who presented with mesial decay and interproximal tartar build-up, for which extraction and scaling to remove tartar deposits were indicated. Following extraction, the usual haemostasis techniques were applied, and postoperative prophylactic antihaemophilic treatment was indicated for 2 or 3 days. The patient presented with moderate bleeding for a few minutes immediately after the procedure. Administration of factor VIII before surgery as well as the patient's favourable pharmacokinetic response allowed for an optimal result. This treatment has afforded patients with haemophilia a better quality of life, and safe and efficient access to invasive surgical procedures.
Keywords: dentistry and oral medicine; haematology (incl blood transfusion); pharmacology and therapeutics.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
