Developing Critical Thinking Skills in Pharmacy Students
- PMID: 30962645
- PMCID: PMC6448513
- DOI: 10.5688/ajpe7033
Developing Critical Thinking Skills in Pharmacy Students
Abstract
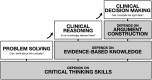
Objective. To review the importance of and barriers to critical thinking and provide evidence-based recommendations to encourage development of these skills in pharmacy students. Findings. Critical thinking (CT) is one of the most desired skills of a pharmacy graduate but there are many challenges to students thinking critically including their own perceptions, poor metacognitive skills, a fixed mindset, a non-automated skillset, heuristics, biases and the fact that thinking is effortful. Though difficult, developing CT skills is not impossible. Research and practice suggest several factors that can improve one's thinking ability: a thoughtful learning environment, seeing or hearing what is done to executive cognitive operations that students can emulate, and guidance and support of their efforts until they can perform on their own. Summary. Teaching CT requires coordination at the curricular level and further to the more discrete level of a lesson and a course. Instructor training is imperative to this process since this intervention has been found to be the most effective in developing CT skills.
Keywords: clinical decision making; course design; critical thinking; metacognition; problem solving.
Figures
References
-
- Abrami PC, Bernard RM, Borokhovski E, et al. Instructional interventions affecting critical thinking skills and dispositions: a stage 1 meta-analysis. Rev Educ Res. 2008;78(4):1102–1134.
-
- Alfaro-LeFevre R. Critical Thinking, Clinical Reasoning, and Clinical Judgment: A Practical Approach. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017.
-
- Hughes R. Patient Safety and Quality: An Evidence-based Handbook for Nurses. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, US Department of Health and Human Services; 2008. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources