<Editors' Choice> Pulmonary Hypertension: Diagnosis, Management, and Treatment
- PMID: 30962652
- PMCID: PMC6433622
- DOI: 10.18999/nagjms.81.1.19
<Editors' Choice> Pulmonary Hypertension: Diagnosis, Management, and Treatment
Abstract
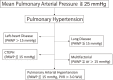
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a hemodynamic state that is characterized by a resting mean pulmonary artery pressure ≧ 25 mmHg. The common forms of PH are pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH), PH caused by left-heart disease, and PH due to lung disease. Previously regarded as untreatable, the treatment of PAH has dramatically advanced since the introduction of the drug epoprostenol in 1999, with three-year survival rates improving from 30%-40% to over 85%. Drugs available for the specific treatment of PAH include endothelin-receptor antagonists, phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors, soluble guanylate cyclase stimulators, prostacyclin analogs, and prostacyclin-receptor agonists. In the past decade, management and treatment of CTEPH have also improved. While pulmonary endarterectomy used to be the only option for the treatment of CTEPH, newer treatments include a soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator, which has proven to be an efficacious targeted therapy. Other cases benefit from balloon pulmonary angioplasty.
Keywords: Pulmonary hypertension; chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH); pulmonary arterial hypertension; pulmonary hypertension (PAH).
Conflict of interest statement
Takahisa Kondo, Naoki Okumura, and Shiro Adachi belong to departments endowed by Actelion Pharmaceuticals Japan, which is part of the Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson.
Figures
References
-
- Simonneau G, Gatzoulis MA, Adatia I, et al. Updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(25 Suppl):D34–41. - PubMed
-
- Barst RJ, Rubin LJ, Long WA, et al. A comparison of continuous intravenous epoprostenol (prostacyclin) with conventional therapy for primary pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1996;334(5):296–301. - PubMed
-
- Galie N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Heart J. 2016;37(1):67–119. - PubMed
-
- Tamura Y, Kumamaru H, Satoh T, et al. Effectiveness and outcome of pulmonary arterial hypertension-specific therapy in Japanese patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circ J. 2017;82(1):275–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
