Long-term efficacy and safety of infliximab and cyclosporine combination therapy for refractory uveoretinitis in Behçet's disease
- PMID: 30962672
- PMCID: PMC6433110
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S198648
Long-term efficacy and safety of infliximab and cyclosporine combination therapy for refractory uveoretinitis in Behçet's disease
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the long-term efficacy and safety of infliximab (IFX) and cyclosporine (CsA) combination therapy for refractory uveoretinitis in Behçet's disease (BD).
Patients and methods: The study involved a retrospective review of the medical records of 11 patients with Behçet's uveoretinitis refractory to conventional treatment who had been treated with IFX+CsA combination therapy. The frequency of ocular inflammatory attacks and a Behçet's disease ocular attack score 24 (BOS24) were used as indices for the evaluation of efficacy during each 6-month period prior to and following initiation of therapy. For the assessment of safety, adverse events (AEs) were recorded throughout the treatment period.
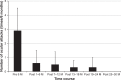
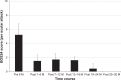
Results: The patients had received IFX+CsA combination therapy for 5.6±2.3 years. The frequency of ocular attacks per 6-month period decreased markedly from 2.9±1.6 during the baseline period to 0.6±0.9 during months 1-6, 0.5±0.9 during months 7-12, 0.3±0.5 during months 13-18, 0.3±0.7 during months 19-24, and 0.0±0.0 thereafter (P=0.003). The BOS24 score per ocular attack significantly decreased from 5.2±2.4 during the baseline period to 1.5±2.1 during months 1-6, 1.7±3.1 during months 7-12, 1.6±2.9 during months 13-18, and 0.4±1.0 during months 19-24 (P=0.002). No serious AEs were observed, with the exception of urinary tract infection and cataract progression. Two patients exhibited transient elevation of the serum creatinine level, which was normalized following a reduction in the dose of CsA.
Conclusion: For refractory Behçet's uveoretinitis, IFX+CsA combination therapy offers a promising treatment option as it appears to have an acceptable safety profile and can reduce the frequency and severity of ocular inflammatory attacks over a long period of time.
Keywords: Behçet’s disease; cyclosporine; efficacy; infliximab; safety; uveitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Nakamura S, Sugita M, Tanaka S, Ohno S. Enhanced production of in vitro tumor necrosis factor-alpha from monocytes in Behcet’s disease. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 1992;96(10):1282–1285. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

