Hexyl alginate derivative, an amphiphilic innovative buccal film-forming material of promising mechanical and release characteristics for the improvement of repaglinide bioavailability
- PMID: 30962675
- PMCID: PMC6432887
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S196425
Hexyl alginate derivative, an amphiphilic innovative buccal film-forming material of promising mechanical and release characteristics for the improvement of repaglinide bioavailability
Abstract
Background: Association of long hydrocarbon chain with alginate molecule imparts surface active properties and increases chain flexibility.
Purpose: This work studied the efficacy of synthesized hexyl alginate derivative as a film-forming material with unique amphiphilic and mechanical properties for the preparation of rapidly disintegrating repaglinide oral films with higher drug release rate and improved bioavailability.
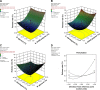
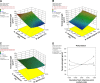
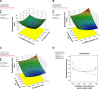
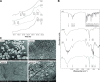
Methods: Alginate hexyl amide derivative was prepared and used in the formulation of oral films by solvent casting technique. Using Box-Behnken experimental design, formulations were optimized at different polymer, plasticizer, and disintegrant levels as independent variables for maximum drug release rate, higher tensile strength, and shortest disintegration time as responses. Optimized film formulae were fully evaluated and subjected to further in vivo bioavailability studies in rabbits.
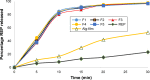
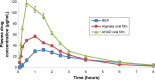
Results: Higher dependency of response results on the selected variables was observed. Optimized formula showed satisfactory tensile strength (145.862 g/cm2), rapid disintegration (22.2 seconds), and higher drug release rate (97.799% within 30 minutes). The drug bioavailability was significantly improved in comparison with plain drug and conventional alginate oral films, where the AUC and Cmax values reached 296.072 μg.h/mL and 116.932 μg/mL in comparison with 164.917 μg.h/mL and 56.568 μg/mL for alginate film and 95.368 μg.h/mL and 31.925 μg/mL for plain drug, respectively. Tmax also showed significant reduction to be only 30 minutes in comparison with 60 minutes for other forms.
Conclusion: This led to the final conclusion that the synthesized alginate derivative is an innovative promising film-forming material with unique mechanical and drug release properties for application in buccal drug delivery especially of Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS) class II drugs to increase solubility and improve bioavailability.
Keywords: BCS class II drugs; Box–Behnken; amphiphilic derivatives of alginate; oral films; repaglinide.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The author reports no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Oledzka E, Sobczak M. Agbo EC, editor. Polymers in the pharmaceutical applications-Natural and bioactive initiators and catalysts in the synthesis of biodegradable and bioresorbable polyesters and polycarbonates. Innovations in Biotechnology: InTech. 2012. [Accessed May 16, 2018]. Available from: http://www.intechopen.com/books/innovations-in-biotechnology/polymers-in....
-
- Farokhzad OC, Jon S, Khademhosseini A, et al. Nanoparticle-aptamer bioconjugates: a new approach for targeting prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64(21):7668–7672. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

