Targeting RET-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer: future prospects
- PMID: 30962732
- PMCID: PMC6433115
- DOI: 10.2147/LCTT.S192830
Targeting RET-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer: future prospects
Abstract
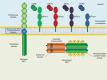
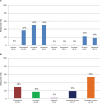
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with mutated or rearranged oncogene drivers can be treated with upfront selective inhibitors achieving higher response rates and longer survival than chemotherapy. The RET gene can undergo chromosomal rearrangements in 1%-2% of all NSCLC patients, involving various upstream fusion partners such as KIF5B, CCDC6, NCOA4, and TRIM33. Many multikinase inhibitors are active against rearranged RET. Cabozantinib, vandetanib, sunitinib, lenvatinib, and nintedanib achieved tumor responses in about 30% of these patients in retrospective studies. Prospective phase II trials investigated the activity and toxicity of cabozantinib, vandetanib, sorafenib, and lenvatinib, and did not reach significantly higher response rates. VEGFR and EGFR inhibition represented the main ways of developing off-target toxicity. An intrinsic resistance emerged according to the type of RET fusion partners, as KIF5B-RET fusion is the most resistant. Also acquired mutations in rearranged RET oncogene developed as resistance to these multikinase inhibitors. Interestingly, RET fusions have been found as a resistance mechanism to EGFR-TKIs in EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients. The combination of EGFR and RET inhibition can overcome this resistance. The limitations in terms of activity and tolerability of the various multikinase inhibitors prompted the investigation of new highly selective RET inhibitors, such as RXDX-105, BLU-667, and LOXO-292. Some data emerged about intracranial antitumor activity of BLU-667 and LOXO-292. If these novel drugs will achieve high activity in RET rearranged NSCLC, also these oncogene-addicted tumors can undergo a significant survival improvement.
Keywords: RET; gene rearrangement; multi-kinase inhibitors; non-small-cell lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Novello S, Barlesi F, Califano R, et al. Metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2016;27(suppl 5):v1–v27. - PubMed
-
- Bronte G, Rizzo S, La Paglia L, et al. Driver mutations and differential sensitivity to targeted therapies: a new approach to the treatment of lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Treat Rev. 2010;36(Suppl 3):S21–S29. - PubMed
-
- Rolfo C, Mack PC, Scagliotti GV, et al. Liquid biopsy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): a statement paper from the IASLC. J Thorac Oncol. 2018;13(9):1248–1268. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi M, Ritz J, Cooper GM. Activation of a novel human transforming gene, RET, by DNA rearrangement. Cell. 1985;42(2):581–588. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

