Scleromyxedema (Arndt - Gottron Syndrome) Developing Under Tenofovir Treatment for Hepatitis B: Unique Presentation in a Bulgarian Patient!
- PMID: 30962839
- PMCID: PMC6447340
- DOI: 10.3889/oamjms.2019.181
Scleromyxedema (Arndt - Gottron Syndrome) Developing Under Tenofovir Treatment for Hepatitis B: Unique Presentation in a Bulgarian Patient!
Abstract
Background: Scleromyxedema, also referred to as the Arndt-Gottron (S-AG) syndrome or the systemic form of Lichen myxedematosus (LM), is a cutaneous mucinosis with a chronic course and high lethality from systemic involvement of other organs and systems. Interesting in several aspects is the association between scleromyxedema and viral hepatitis about: 1) hepatitis virus infection as a possible etiological factor for the development of scleromyxedema, 2) antiretroviral therapy for the treatment of hepatitis as a method of reversing scleromyxedema and 3) antiviral drugs as inducers of scleromyxedema.
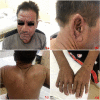
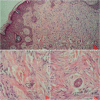
Case report: We present a 53-year old patient who for nine months had been on tenofovir disoproxil 245 mg (0-0-1) therapy for chronic hepatitis B. Three months after the start of antiviral therapy (i.e. for a period of 6 months), the patient observed swelling, itching and hardening of the skin on the face, ears and hands, which subsequently spread throughout the trunk. Subsequent histological study of a skin biopsy revealed changes of scleromyxedema at an advanced stage, though immunoelectrophoresis of serum and urine excluded the presence of paraproteinaemia or para proteinuria. Systemic antihistamine and topical corticosteroid therapy were instituted. Bone involvement with possible plasmacytoma was excluded, and a myelogram showed evidence of an erythroblastic reaction of bone marrow.
Conclusion: We believe that drug-induced scleromyxedema is a rare but possible phenomenon. We describe the first case of tenofovir-induced scleromyxedema within the framework of chronic hepatitis B treatment.
Keywords: Arndt - Gottron syndrome; Diabetes mellitus; Hepatitis B; Pathogenetic relationship; Scleromyxedema; Survival benefit; Tenofovir; Treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Dermato-neuro syndrome-an acute and life-threatening complication of scleromyxedema Arndt-Gottron].Dermatologie (Heidelb). 2023 Aug;74(8):618-620. doi: 10.1007/s00105-023-05159-w. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Dermatologie (Heidelb). 2023. PMID: 37284981 Free PMC article. German.
-
[Efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin in Arndt-Gottron scleromyxedema].Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2009 Apr;136(4):330-6. doi: 10.1016/j.annder.2008.06.011. Epub 2008 Dec 24. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2009. PMID: 19361699 French.
-
Early onset of scleromyxedema Arndt-Gottron associated with a monoclonal gammapathy: Successful treatment with intravenous immunoglobulins.Clin Case Rep. 2022 Aug 3;10(8):e6122. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.6122. eCollection 2022 Aug. Clin Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35937020 Free PMC article.
-
[Arndt-Gottron scleromyxedema. Case report and review of therapeutic possibilities].Hautarzt. 1992 Mar;43(3):152-7. Hautarzt. 1992. PMID: 1577603 Review. German.
-
Lichen myxedematosus (papular mucinosis): new concepts and perspectives for an old disease.Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2006 Jun;25(2):100-4. doi: 10.1016/j.sder.2006.04.001. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2006. PMID: 16908401 Review.
References
-
- Rongioletti F, Rebora A. Updated classification of papular mucinosis, lichen myxedematosus, and scleromyxedema. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44(2):273–81. https://doi.org/10.1067/mjd.2001.111630 PMid:11174386. - PubMed
-
- Sala A, Cunha P, Pinto C, Alves C, Paiva I, Araujo A. Scleromyxedema:clinical diagnosis and autopsy findings. A Bras Dermatol. 2016;91(5 Suppl 1):48–50. https://doi.org/10.1590/abd1806-4841.20164527 PMid:28300892 PMCid:PMC5324991. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saniee S, Davarnia G. Scleromyxedema without Paraproteinemia:Treatment with Thalidomide and Prednisolone. Case Rep Dermatol. 2016;8(3):327–332. https://doi.org/10.1159/000452319 PMid:27990110 PMCid:PMC5156886. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rongioletti F, Merlo G, Cinotti E, Fausti V, Cozzani E, Cribier B, Metze D, Calonje E, Kanitakis J, Kempf W, Stefanato C, Marinho E, Parodi A. Scleromyxedema:a multicenter study of characteristics, comorbidities, course, and therapy in 30 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;69(1):66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2013.01.007 PMid:23453242. - PubMed
-
- Smith J, Kalimullah F, Erickson C, Peng L. Scleromyxedema secondary to hepatitis C virus and successfully treated with antiviral therapy. Dermatol Online J. 2015;21(9) - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
