Apical periodontitis associated with a calculus-like deposit: A case report of a rare fan-shaped manifestation
- PMID: 30962929
- PMCID: PMC6434093
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amsu.2019.03.003
Apical periodontitis associated with a calculus-like deposit: A case report of a rare fan-shaped manifestation
Abstract
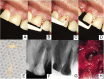
Introduction: Bacterial biofilms can be calcified. Granulomas or cystic lesions are the most commonly found entities in endodontics. Surprisingly, this case report presents a rare radiopaque image, in a fan shape, of a calculus-like deposit in the periapical region of the maxillary left central incisor.
Case presentation: A 34-year-old male, with a history of trauma, presented with apical periodontitis associated with an uncommon image, similar to a calculus-like deposit adhered to the apical region of the maxillary left central incisor. Nonsurgical endodontic intervention was performed, followed by apicoectomy and histopathological analysis of the collected material. The results of the biopsy were not compatible with a cyst or granuloma but showed fibrous connective tissue with calcified areas.
Discussion: Correct diagnosis in endodontics is possible with a well-conducted anamnesis, complementary imaging exams and, in some cases, histopathological analysis. The periapical calculus-like deposit, associated with a periapical radiolucent lesion, was a result of the body's fight for healing, producing unusual radiopacity.
Conclusion: The presence of the calculus-like deposit in a fan shape at the root surface represented dystrophic calcification as a manifestation of the attempt to heal. In the present case, apicoectomy and tissue biopsy for histological evaluation were fundamental for the correct diagnosis.
Keywords: Apicoectomy; Biofilms; Cone-beam computed tomography; Dental radiography; Periapical periodontitis.
Figures


References
-
- Aggarwal V., Singla M. Use of computed tomography scans and ultrasound in differential diagnosis and evaluation of nonsurgical management of periapical lesions. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2010;109:917–923. https://doi:10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.12.055 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shekhar V., Shashikala K. Cone beam computed tomography evaluation of the diagnosis, treatment planning, and long-term followup of large periapical lesions treated by endodontic surgery: two case reports. Case Rep. Dent. 2013;2013:1–12. https://doi:10.1155/2013/564392 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ricucci D., Siqueira J.F., Jr., Lopes W.S.P., Vieira A.R., Rôças I.N. Extraradicular infection as the cause of persistent symptoms: a case series. J. Endod. 2015;41:265–273. https://doi:10.1016/j.joen.2014.08.020 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Soares A.J., Souza G.A., Pereira A.C., Vargas-Neto J., Zaia A.A., Silva E.J.N.L. Frequency of root resorption following trauma to permanent teeth. J. Oral Sci. 2015;57:73–78. https://doi:10.2334/josnusd.57.73 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang J., Jiang Y., Chen W., Zhu C., Liang J. Bacterial flora and extraradicular biofilm associated with the apical segment of teeth with post-treatment apical periodontitis. J. Endod. 2012;38:954–959. https://doi:10.1016/j.joen.2012.03.004 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

