A Frizzled-Like Cysteine-Rich Domain in Glypican-3 Mediates Wnt Binding and Regulates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tumor Growth in Mice
- PMID: 30963603
- PMCID: PMC6783318
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.30646
A Frizzled-Like Cysteine-Rich Domain in Glypican-3 Mediates Wnt Binding and Regulates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tumor Growth in Mice
Abstract
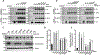
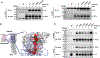
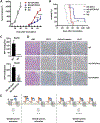
Wnt signaling is one of the key regulators of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tumor progression. In addition to the classical receptor frizzled (FZD), various coreceptors including heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) are involved in Wnt activation. Glypican-3 (GPC3) is an HSPG that is overexpressed in HCC and functions as a Wnt coreceptor that modulates HCC cell proliferation. These features make GPC3 an attractive target for liver cancer therapy. However, the precise interaction of GPC3 and Wnt and how GPC3, Wnt, and FZD cooperate with each other are poorly understood. In this study, we established a structural model of GPC3 containing a putative FZD-like cysteine-rich domain at its N-terminal lobe. We found that F41 and its surrounding residues in GPC3 formed a Wnt-binding groove that interacted with the middle region located between the lipid thumb domain and the index finger domain of Wnt3a. Mutating residues in this groove significantly inhibited Wnt3a binding, β-catenin activation, and the transcriptional activation of Wnt-dependent genes. In contrast with the heparan sulfate chains, the Wnt-binding groove that we identified in the protein core of GPC3 seemed to promote Wnt signaling in conditions when FZD was not abundant. Specifically, blocking this domain using an antibody inhibited Wnt activation. In HCC cells, mutating residue F41 on GPC3 inhibited activation of β-catenin in vitro and reduced xenograft tumor growth in nude mice compared with cells expressing wild-type GPC3. Conclusion: Our investigation demonstrates a detailed interaction of GPC3 and Wnt3a, reveals the precise mechanism of GPC3 acting as a Wnt coreceptor, and provides a potential target site on GPC3 for Wnt blocking and HCC therapy.
© 2019 by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest:
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures


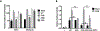
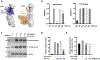

References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Cancer C, Fitzmaurice C, Allen C, Barber RM, Barregard L, Bhutta ZA, Brenner H, et al. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-years for 32 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol 2017;3:524–548. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2012;379:1245–1255. - PubMed
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

