Extracellular RNA in viral-host interactions: Thinking outside the cell
- PMID: 30963709
- PMCID: PMC6617787
- DOI: 10.1002/wrna.1535
Extracellular RNA in viral-host interactions: Thinking outside the cell
Abstract
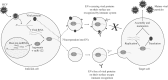
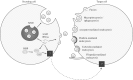
Small RNAs and their associated RNA interference (RNAi) pathways underpin diverse mechanisms of gene regulation and genome defense across all three kingdoms of life and are integral to virus-host interactions. In plants, fungi and many animals, an ancestral RNAi pathway exists as a host defense mechanism whereby viral double-stranded RNA is processed to small RNAs that enable recognition and degradation of the virus. While this antiviral RNAi pathway is not generally thought to be present in mammals, other RNAi mechanisms can influence infection through both viral- and host-derived small RNAs. Furthermore, a burgeoning body of data suggests that small RNAs in mammals can function in a non-cell autonomous manner to play various roles in cell-to-cell communication and disease through their transport in extracellular vesicles. While vesicular small RNAs have not been proposed as an antiviral defense pathway per se, there is increasing evidence that the export of host- or viral-derived RNAs from infected cells can influence various aspects of the infection process. This review discusses the current knowledge of extracellular RNA functions in viral infection and the technical challenges surrounding this field of research. This article is categorized under: Regulatory RNAs/RNAi/Riboswitches > Regulatory RNAs RNA in Disease and Development > RNA in Disease Regulatory RNAs/RNAi/Riboswitches > RNAi: Mechanisms of Action.
Keywords: RNA interference; extracellular RNA; extracellular vesicle; host-pathogen; microRNA.
© 2019 The Authors. WIREs RNA published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of RNase L-dependent, 3'-end-modified, viral small RNAs in Sindbis virus-infected mammalian cells.mBio. 2013 Nov 19;4(6):e00698-13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00698-13. mBio. 2013. PMID: 24255120 Free PMC article.
-
The RNAi Universe in Fungi: A Varied Landscape of Small RNAs and Biological Functions.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2017 Sep 8;71:371-391. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-090816-093352. Epub 2017 Jun 28. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28657888 Review.
-
Small RNA-based antimicrobial immunity.Nat Rev Immunol. 2019 Jan;19(1):31-44. doi: 10.1038/s41577-018-0071-x. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30301972 Review.
-
The evolving world of small RNAs from RNA viruses.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016 Sep;7(5):575-88. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1351. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016. PMID: 27046163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metagenomic sequencing suggests a diversity of RNA interference-like responses to viruses across multicellular eukaryotes.PLoS Genet. 2018 Jul 30;14(7):e1007533. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007533. eCollection 2018 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 30059538 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Viral Replication and Pathogenesis and Their Potential Role in Therapeutic Intervention.Viruses. 2020 Aug 13;12(8):887. doi: 10.3390/v12080887. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32823684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cryo-EM analysis reveals human SID-1 transmembrane family member 1 dynamics underlying lipid hydrolytic activity.Commun Biol. 2024 May 29;7(1):664. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06346-8. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 38811802 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing Benzo[a]pyrene Adducts in Transfer RNAs Using Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS).Biomedicines. 2023 Dec 11;11(12):3270. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11123270. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38137491 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Affecting the Tissue Damaging Consequences of Viral Infections.Front Microbiol. 2019 Oct 4;10:2314. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02314. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31636623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interrogating Cellular Communication in Cancer with Genetically Encoded Imaging Reporters.Radiol Imaging Cancer. 2020 Jul 31;2(4):e190053. doi: 10.1148/rycan.2020190053. Radiol Imaging Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32803164 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

