Controlled Release of Lysozyme from Double-Walled Poly(Lactide-Co-Glycolide) (PLGA) Microspheres
- PMID: 30965787
- PMCID: PMC6418743
- DOI: 10.3390/polym9100485
Controlled Release of Lysozyme from Double-Walled Poly(Lactide-Co-Glycolide) (PLGA) Microspheres
Abstract
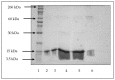
Double-walled microspheres based on poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) are potential delivery systems for reducing a very high initial burst release of encapsulated protein and peptide drugs. In this study, double-walled microspheres made of glucose core, hydroxyl-terminated poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (Glu-PLGA), and carboxyl-terminated PLGA were fabricated using a modified water-in-oil-in-oil-in-water (w1/o/o/w2) emulsion solvent evaporation technique for the controlled release of a model protein, lysozyme. Microspheres size, morphology, encapsulation efficiency, lysozyme in vitro release profiles, bioactivity, and structural integrity, were evaluated. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images revealed that double-walled microspheres comprising of Glu-PLGA and PLGA with a mass ratio of 1:1 have a spherical shape and smooth surfaces. A statistically significant increase in the encapsulation efficiency (82.52% ± 3.28%) was achieved when 1% (w/v) polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and 2.5% (w/v) trehalose were incorporated in the internal and external aqueous phase, respectively, during emulsification. Double-walled microspheres prepared together with excipients (PVA and trehalose) showed a better control release of lysozyme. The released lysozyme was fully bioactive, and its structural integrity was slightly affected during microspheres fabrication and in vitro release studies. Therefore, double-walled microspheres made of Glu-PLGA and PLGA together with excipients (PVA and trehalose) provide a controlled and sustained release for lysozyme.
Keywords: controlled release; double-walled microspheres; drug delivery; poly(lactide-co-glycolide); therapeutic proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Zimmer A., Kreuter J. Microspheres and nanoparticles used in ocular delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1995;16:61–73. doi: 10.1016/0169-409X(95)00017-2. - DOI
-
- Samadi N., Abbadessa A., Di Stefano A., van Nostrum C.F., Vermonden T., Rahimian S., Teunissen E.A., van Steenbergen M.J., Amidi M., Hennink W.E. The effect of lauryl capping group on protein release and degradation of poly(d,l-lactic-co-glycolic acid) particles. J. Control. Release. 2013;172:436–443. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.05.034. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

