Predicting Islet Cell Autoimmunity and Type 1 Diabetes: An 8-Year TEDDY Study Progress Report
- PMID: 30967432
- PMCID: PMC6609953
- DOI: 10.2337/dc18-2282
Predicting Islet Cell Autoimmunity and Type 1 Diabetes: An 8-Year TEDDY Study Progress Report
Abstract
Objective: Assessment of the predictive power of The Environmental Determinants of Diabetes in the Young (TEDDY)-identified risk factors for islet autoimmunity (IA), the type of autoantibody appearing first, and type 1 diabetes (T1D).
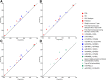
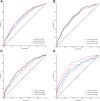
Research design and methods: A total of 7,777 children were followed from birth to a median of 9.1 years of age for the development of islet autoantibodies and progression to T1D. Time-dependent sensitivity, specificity, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were calculated to provide estimates of their individual and collective ability to predict IA and T1D.
Results: HLA genotype (DR3/4 vs. others) was the best predictor for IA (Youden's index J = 0.117) and single nucleotide polymorphism rs2476601, in PTPN22, was the best predictor for insulin autoantibodies (IAA) appearing first (IAA-first) (J = 0.123). For GAD autoantibodies (GADA)-first, weight at 1 year was the best predictor (J = 0.114). In a multivariate model, the area under the ROC curve (AUC) was 0.678 (95% CI 0.655, 0.701), 0.707 (95% CI 0.676, 0.739), and 0.686 (95% CI 0.651, 0.722) for IA, IAA-first, and GADA-first, respectively, at 6 years. The AUC of the prediction model for T1D at 3 years after the appearance of multiple autoantibodies reached 0.706 (95% CI 0.649, 0.762).
Conclusions: Prediction modeling statistics are valuable tools, when applied in a time-until-event setting, to evaluate the ability of risk factors to discriminate between those who will and those who will not get disease. Although significantly associated with IA and T1D, the TEDDY risk factors individually contribute little to prediction. However, in combination, these factors increased IA and T1D prediction substantially.
© 2019 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 DK063821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063790/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001082/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000064/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN267200700014C/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK095300/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK117483/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK112243/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK106955/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK100238/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

