Evaluation of an untargeted nano-liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry approach to expand coverage of low molecular weight dissolved organic matter in Arctic soil
- PMID: 30967565
- PMCID: PMC6456581
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-42118-9
Evaluation of an untargeted nano-liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry approach to expand coverage of low molecular weight dissolved organic matter in Arctic soil
Abstract
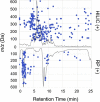
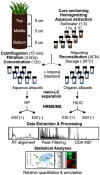
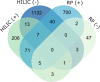
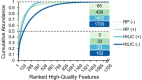
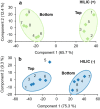
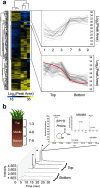
Characterizing low molecular weight (LMW) dissolved organic matter (DOM) in soils and evaluating the availability of this labile pool is critical to understanding the underlying mechanisms that control carbon storage or release across terrestrial systems. However, due to wide-ranging physicochemical diversity, characterizing this complex mixture of small molecules and how it varies across space remains an analytical challenge. Here, we evaluate an untargeted approach to detect qualitative and relative-quantitative variations in LMW DOM with depth using water extracts from a soil core from the Alaskan Arctic, a unique system that contains nearly half the Earth's terrestrial carbon and is rapidly warming due to climate change. We combined reversed-phase and hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography, and nano-electrospray ionization coupled with high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry in positive- and negative-ionization mode. The optimized conditions were sensitive, robust, highly complementary, and enabled detection and putative annotations of a wide range of compounds (e.g. amino acids, plant/microbial metabolites, sugars, lipids, peptides). Furthermore, multivariate statistical analyses revealed subtle but consistent and significant variations with depth. Thus, this platform is useful not only for characterizing LMW DOM, but also for quantifying relative variations in LMW DOM availability across space, revealing hotspots of biogeochemical activity for further evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Schuur EAG, et al. Vulnerability of permafrost carbon to climate change: Implications for the global carbon cycle. Bioscience. 2008;58:701–714. doi: 10.1641/b580807. - DOI
-
- Sjogersten S, et al. Organic matter chemistry controls greenhouse gas emissions from permafrost peatlands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016;98:42–53. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.03.016. - DOI
-
- Yang Z, Wullschleger SD, Liang L, Graham DE, Gu B. Effects of warming on the degradation and production of low-molecular-weight labile organic carbon in an Arctic tundra soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016;95:202–211. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.12.022. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

