Electrical impulse effects on degenerative human annulus fibrosus model to reduce disc pain using micro-electrical impulse-on-a-chip
- PMID: 30967598
- PMCID: PMC6456732
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-42320-9
Electrical impulse effects on degenerative human annulus fibrosus model to reduce disc pain using micro-electrical impulse-on-a-chip
Abstract
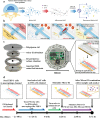
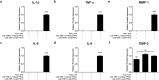
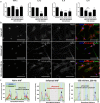
Electrical stimulation of cells and tissues for therapeutic benefit is a well-established method. Although animal studies can emulate the complexity of an organism's physiology, lab-on-a-chip platforms provide a suitable primary model for follow-up animal studies. Thus, inexpensive and easy-to-use platforms for in vitro human cell studies are required. In the present study, we designed a micro-electrical impulse (micro-EI)-on-a-chip (micro-EI-chip), which can precisely control electron density and adjust the frequency based on a micro-EI. The micro-EI-chip can stimulate cells at various micro-EI densities (0-500 mV/mm) and frequencies (0-300 Hz), which enables multiple co-culture of different cell types with or without electrical stimulation. As a proof-of-concept study, a model involving degenerative inflamed human annulus fibrosus (hAF) cells was established in vitro and the effects of micro-EI on inflamed hAF cells were evaluated using the micro-EI-chip. Stimulation of the cells (150 mV/mm at 200 Hz) inhibited the secretion of inflammatory cytokines and downregulated the activities of extracellular matrix-modifying enzymes and matrix metalloproteinase-1. These results show that micro-EI stimulation could affect degenerative diseases based on inflammation, implicating the micro-EI-chip as being useful for basic research of electroceuticals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Photobiomodulation on human annulus fibrosus cells during the intervertebral disk degeneration: extracellular matrix-modifying enzymes.Lasers Med Sci. 2016 May;31(4):767-77. doi: 10.1007/s10103-016-1923-x. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Lasers Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 26987527
-
Development of a two-step protocol for culture expansion of human annulus fibrosus cells with TGF-β1 and FGF-2.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016 Jul 12;7(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s13287-016-0332-1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27405858 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of biphasic electrical current stimulation on IL-1β-stimulated annulus fibrosus cells using in vitro microcurrent generating chamber system.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013 Oct 15;38(22):E1368-76. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3182a211e3. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013. PMID: 23823576
-
Annulus fibrosus cell phenotypes in homeostasis and injury: implications for regenerative strategies.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019 Apr;1442(1):61-78. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13964. Epub 2018 Sep 14. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019. PMID: 30604562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repair and Regenerative Therapies of the Annulus Fibrosus of the Intervertebral Disc.J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2016 Feb;26(2):138-44. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2016. PMID: 26876403 Review.
Cited by
-
Research Progress of Electrical Stimulation in Ischemic Heart Disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Nov 3;8:761877. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.761877. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34805318 Free PMC article.
-
Can self-powered piezoelectric materials be used to treat disc degeneration by means of electrical stimulation?Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 May 9;12:1397261. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1397261. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38784767 Free PMC article.
-
Electrical stimulation promoting the angiogenesis in diabetic rat perforator flap through attenuating oxidative stress-mediated inflammation and apoptosis.PeerJ. 2024 Jan 31;12:e16856. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16856. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38313008 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidic Electroceuticals Platform for Therapeutic Strategies of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Effects of Electrical Stimulation on Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells under Inflammatory Conditions.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 4;23(17):10122. doi: 10.3390/ijms231710122. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077518 Free PMC article.
-
Acid external and internal environment exchange the Oreochromis niloticus tissue immune gene expression compared to the mouse macrophage polarization model.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 26;13:1012078. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1012078. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36225935 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

