Removing melatonin receptor type 1 signaling leads to selective leptin resistance in the arcuate nucleus
- PMID: 30968433
- PMCID: PMC6687516
- DOI: 10.1111/jpi.12580
Removing melatonin receptor type 1 signaling leads to selective leptin resistance in the arcuate nucleus
Abstract
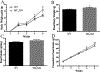
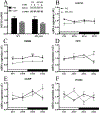
Recent studies have highlighted the involvement of melatonin in the regulation of energy homeostasis. In this study, we report that mice lacking melatonin receptor 1 (MT1 KO) gained more weight, had a higher cumulative food intake, and were more hyperphagic after fasting compared to controls (WT). In response to a leptin injection, MT1 KO mice showed a diminished reduction in body weight and food intake. To evaluate hypothalamic leptin signaling, we tested leptin-induced phosphorylation of the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3). Leptin failed to induce STAT3 phosphorylation in MT1 KO mice beyond levels observed in mice injected with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Furthermore, STAT3 phosphorylation within the arcuate nucleus (ARH) was decreased in MT1 KO mice. Leptin receptor mRNA levels in the hypothalamus of MT1 KO were significantly reduced (about 50%) compared to WT. This study shows that: (a) MT1 deficiency causes weight gain and increased food intake; (b) a lack of MT1 signaling induces leptin resistance; (c) leptin resistance is ARH region-specific; and (d) leptin resistance is likely due to down-regulation of the leptin receptor. Our data demonstrate that MT1 signaling is an important modulator of leptin signaling.
Keywords: leptin receptor; leptin resistance; melatonin; melatonin receptor 1; metabolism; obesity.
© 2019 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures




References
-
- CIPOLLA-NETO J, AMARAL FG, AFECHE SC et al. Melatonin, energy metabolism, and obesity: a review. Journal of pineal research 2014; 56:371–81. - PubMed
-
- REPPERT SM Melatonin receptors: molecular biology of a new family of G protein-coupled receptors. Journal of biological rhythms 1997; 12:528–31. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- SC2 GM116760/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY026291/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS034194/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- G12 RR003034/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T-103104/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R25 MD007589/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- S21 MD000101/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR026137/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- G12 MD007602/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS083932/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- GM116760/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- EY026291/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL103104/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

