Patient-Reported Outcome Results From the Open-Label, Randomized Phase III Myeloma X Trial Evaluating Salvage Autologous Stem-Cell Transplantation in Relapsed Multiple Myeloma
- PMID: 30969846
- PMCID: PMC6858007
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.18.01006
Patient-Reported Outcome Results From the Open-Label, Randomized Phase III Myeloma X Trial Evaluating Salvage Autologous Stem-Cell Transplantation in Relapsed Multiple Myeloma
Abstract
Purpose: Salvage autologous stem-cell transplantation (sASCT) in patients with multiple myeloma (MM) relapsing after a prior autologous stem-cell transplantation leads to increased remission duration and overall survival. We report a comprehensive study on patient-reported outcomes, including quality of life (QoL) and pain in sASCT.
Methods: Patients were randomly assigned to either sASCT or nontransplantation consolidation (NTC). Pain and QoL were assessed as secondary outcomes using validated QoL instruments (European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-C30 and myeloma-specific module, QLQ-MY20; the Brief Pain Inventory [Short Form]; and the Leeds Assessment of Neuropathic Symptoms and Signs [Self-Assessment] scale).
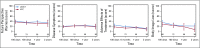
Results: A total of 288 patients (> 96%) consented to the QoL substudy. The median follow-up was 52 months. The European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-C30 Global health status scores were higher (better) in the NTC group at 100 days after random assignment (P = .0496), but not at later time points. Pain interference was higher (worse) in the sASCT group than in the NTC group at 6 months after random assignment (P = .0267), with patients with sASCT reporting higher scores for Pain interference with daily living for up to 2 years after random assignment. Patients reporting lower concerns about adverse effects of treatment after sASCT had a time to progression advantage.
Conclusion: Patients with sASCT with relapsed MM demonstrated a comparative reduction in QoL and greater impact of treatment adverse effects lasting for 6 months and up to 2 years for pain, after which patients who had received sASCT reported better outcomes. Patients who experienced lower adverse effects after sASCT had longer time to progression and overall survival, showing the need to improve symptom management peritransplantation. To our knowledge, this study provides the most comprehensive picture of QoL before and after sASCT in patients with relapsed MM.
Figures

Comment in
-
Importance of Assessing Patient-Reported Outcomes With Salvage Autologous Transplantation in Relapsed Multiple Myeloma.J Clin Oncol. 2019 Jul 1;37(19):1598-1600. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00865. Epub 2019 May 14. J Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31084545 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Attal M, Harousseau JL. Role of autologous stem-cell transplantation in multiple myeloma. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2007;20:747–759. - PubMed
-
- Cavo M, Tacchetti P, Patriarca F, et al. Bortezomib with thalidomide plus dexamethasone compared with thalidomide plus dexamethasone as induction therapy before, and consolidation therapy after, double autologous stem-cell transplantation in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: A randomised phase 3 study. Lancet. 2010;376:2075–2085. - PubMed
-
- Sonneveld P, Schmidt-Wolf IG, van der Holt B, et al. Bortezomib induction and maintenance treatment in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: Results of the randomized phase III HOVON-65/ GMMG-HD4 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:2946–2955. - PubMed
-
- Cook G, Liakopoulou E, Pearce R, et al. Factors influencing the outcome of a second autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT) in relapsed multiple myeloma: A study from the British Society of Blood and Marrow Transplantation Registry. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2011;17:1638–1645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

