Randomized Trial of Verubecestat for Prodromal Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 30970186
- PMCID: PMC6776078
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1812840
Randomized Trial of Verubecestat for Prodromal Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
Background: Prodromal Alzheimer's disease offers an opportunity to test the effect of drugs that modify the deposition of amyloid in the brain before the onset of dementia. Verubecestat is an orally administered β-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE-1) inhibitor that blocks production of amyloid-beta (Aβ). The drug did not prevent clinical progression in a trial involving patients with mild-to-moderate dementia due to Alzheimer's disease.
Methods: We conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 104-week trial to evaluate verubecestat at doses of 12 mg and 40 mg per day, as compared with placebo, in patients who had memory impairment and elevated brain amyloid levels but whose condition did not meet the case definition of dementia. The primary outcome was the change from baseline to week 104 in the score on the Clinical Dementia Rating Scale-Sum of Boxes (CDR-SB; scores range from 0 to 18, with higher scores indicating worse cognition and daily function). Secondary outcomes included other assessments of cognition and daily function.
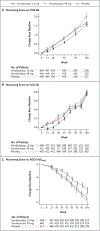
Results: The trial was terminated for futility after 1454 patients had been enrolled; 485 had been assigned to receive verubecestat at a dose of 12 mg per day (the 12-mg group), 484 to receive verubecestat at a dose of 40 mg per day (the 40-mg group), and 485 to receive placebo. A total of 234 patients, 231 patients, and 239 patients per group, respectively, completed 104 weeks of the trial regimen. The estimated mean change from baseline to week 104 in the CDR-SB score was 1.65 in the 12-mg group, 2.02 in the 40-mg group, and 1.58 in the placebo group (P = 0.67 for the comparison between the 12-mg group and the placebo group and P = 0.01 for the comparison between the 40-mg group and the placebo group), suggesting a worse outcome in the higher-dose group than in the placebo group. The estimated rate of progression to dementia due to Alzheimer's disease was 24.5, 25.5, and 19.3 events per 100 patient-years in the 12-mg group, the 40-mg group, and the placebo group, respectively (hazard ratio for 40 mg vs. placebo, 1.38; 97.51% confidence interval, 1.07 to 1.79, not adjusted for multiple comparisons), favoring placebo. Adverse events were more common in the verubecestat groups than in the placebo group.
Conclusions: Verubecestat did not improve clinical ratings of dementia among patients with prodromal Alzheimer's disease, and some measures suggested that cognition and daily function were worse among patients who received verubecestat than among those who received placebo. (Funded by Merck Sharp & Dohme; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT01953601.).
Copyright © 2019 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures
Comment in
-
Lowering of Amyloid-Beta by β-Secretase Inhibitors - Some Informative Failures.N Engl J Med. 2019 Apr 11;380(15):1476-1478. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1903193. N Engl J Med. 2019. PMID: 30970194 No abstract available.
-
Preliminary Results of a Trial of Atabecestat in Preclinical Alzheimer's Disease.N Engl J Med. 2019 Apr 11;380(15):1483-1485. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1813435. N Engl J Med. 2019. PMID: 30970197 No abstract available.
-
Drug-induced reductions in brain amyloid-β levels may adversely affect cognition and behavior by a disruption of functional connectivity homeostasis.Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2019 Aug;9(4):189-191. doi: 10.2217/nmt-2019-0013. Epub 2019 Jul 24. Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2019. PMID: 31337272 No abstract available.
-
Verubecestat for Prodromal Alzheimer's Disease.N Engl J Med. 2019 Jul 25;381(4):388. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1906679. N Engl J Med. 2019. PMID: 31340105 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Masters CL, Bateman R, Blennow K, Rowe CC, Sperling RA, Cummings JL. Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2015;1:15056. - PubMed
-
- Scott JD, Li SW, Brunskill AP, et al. Discovery of the 3-imino-1,2,4-thiadiazi-nane 1,1-dioxide derivative verubecestat (MK-8931) — a 0-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 inhibitor for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J Med Chem 2016;59:10435–50. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy ME, Stamford AW, Chen X, et al. The BACE1 inhibitor verubecestat (MK-8931) reduces CNS β-amyloid in animal models and in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Sci Transl Med 2016;8: 363ra150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
