A Novel Heterogalactan from Antrodia camphorata and Anti-Angiogenic Activity of Its Sulfated Derivative
- PMID: 30970906
- PMCID: PMC6432100
- DOI: 10.3390/polym9060228
A Novel Heterogalactan from Antrodia camphorata and Anti-Angiogenic Activity of Its Sulfated Derivative
Abstract
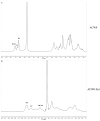
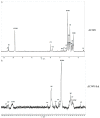
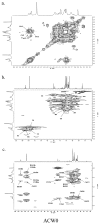
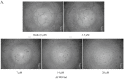
A heterogalactan, named ACW0, was extracted from Antrodia camphorata and purified by anion exchange and gel permeation chromatography. It was composed of galactose (94.98%), traces of mannose (2.41%), and fucose (2.61%), with its molecular weight estimated to be 13.5 k Da. The polysaccharide ACW0 was shown to be a mannofucogalactan with a backbone chain of α-d-1,6-linked Gal, attached by a non-reducing terminal α-d-Man and α-l-Fuc on C-2 of nearly every six α-d-1,6-linked Gal residues. A sulfated polysaccharide, ACW0-Sul was achieved by the chlorosulfonic acid-pyridine method. Compared with the native polysaccharide, ACW0-Sul could disrupt tube formation and migration as well as cell growth of human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1) dose-dependently. Further studies revealed that phosphorylation of Extracellular Regulated Protein Kinases (Erk) and Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) were significantly inhibited by ACW0-Sul. These results suggested that ACW0-Sul could be a potent candidate for anti-angiogenic agent development.
Keywords: Antrodia camphorata; anti-angiogenesis; mannofucogalactan; sulfated polysaccharide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Qiu H., Yang B., Pei Z.C., Zhang Z., Ding K. WSS25 inhibits growth of xenografted hepatocellular cancer cells in nude mice by disrupting angiogenesis via blocking bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)/Smad/Id1 signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2010;285:32638–32646. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.105544. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

