Glucose Oxidase-Based Glucose-Sensitive Drug Delivery for Diabetes Treatment
- PMID: 30970930
- PMCID: PMC6432078
- DOI: 10.3390/polym9070255
Glucose Oxidase-Based Glucose-Sensitive Drug Delivery for Diabetes Treatment
Abstract
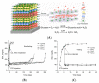
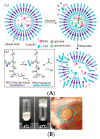
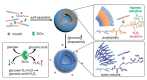
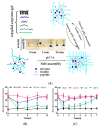
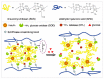
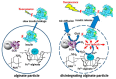
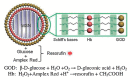
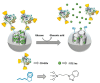
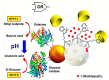
The glucose-sensitive drug delivery systems based on glucose oxidase (GOD), which exhibit highly promising applications in diabetes therapy, have attracted much more interest in recent years. The self-regulated drug delivery systems regulate drug release by glucose concentration automatically and continuously to control the blood glucose level (BGL) in normoglycemic state. This review covers the recent advances at the developments of GOD-based glucose-sensitive drug delivery systems and their in vivo applications for diabetes treatment. The applications of GOD-immobilized platforms, such as self-assembly layer-by-layer (LbL) films and polymer vesicles, cross-linking hydrogels and microgels, hybrid mesoporous silica nanoparticles, and microdevices fabricated with insulin reservoirs have been surveyed. The glucose-sensitive drug delivery systems based on GOD are expected to be a typical candidate for smart platforms for potential applications in diabetes therapy.
Keywords: diabetes therapy; drug delivery; glucose oxidase; glucose sensitivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Zhao L., Xiao C., Ding J., Zhuang X., Gai G., Wang L., Chen X. Competitive binding-accelerated insulin release from a polypeptide nanogel for potential therapy of diabetes. Polym. Chem. 2015;6:3807–3815. doi: 10.1039/C5PY00207A. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

