Multicolor multiscale brain imaging with chromatic multiphoton serial microscopy
- PMID: 30971684
- PMCID: PMC6458155
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-09552-9
Multicolor multiscale brain imaging with chromatic multiphoton serial microscopy
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Multicolor multiscale brain imaging with chromatic multiphoton serial microscopy.Nat Commun. 2019 May 9;10(1):2160. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10225-w. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31073140 Free PMC article.
Abstract
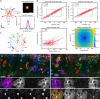
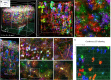
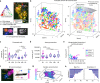
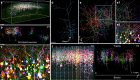
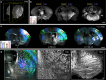
Large-scale microscopy approaches are transforming brain imaging, but currently lack efficient multicolor contrast modalities. We introduce chromatic multiphoton serial (ChroMS) microscopy, a method integrating one-shot multicolor multiphoton excitation through wavelength mixing and serial block-face image acquisition. This approach provides organ-scale micrometric imaging of spectrally distinct fluorescent proteins and label-free nonlinear signals with constant micrometer-scale resolution and sub-micron channel registration over the entire imaged volume. We demonstrate tridimensional (3D) multicolor imaging over several cubic millimeters as well as brain-wide serial 2D multichannel imaging. We illustrate the strengths of this method through color-based 3D analysis of astrocyte morphology and contacts in the mouse cerebral cortex, tracing of individual pyramidal neurons within densely Brainbow-labeled tissue, and multiplexed whole-brain mapping of axonal projections labeled with spectrally distinct tracers. ChroMS will be an asset for multiscale and system-level studies in neuroscience and beyond.
Conflict of interest statement
E.B., P.M., and W.S. are co-authors of a patent that describes multicolor two-photon excitation by wavelength mixing (FR1250990). The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Chromatic multiphoton imaging of the whole brain.Nat Methods. 2019 Jun;16(6):459. doi: 10.1038/s41592-019-0444-5. Nat Methods. 2019. PMID: 31147644 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

