Modulation of Respiratory System by Limb Muscle Afferents in Intact and Injured Spinal Cord
- PMID: 30971888
- PMCID: PMC6443963
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00289
Modulation of Respiratory System by Limb Muscle Afferents in Intact and Injured Spinal Cord
Abstract
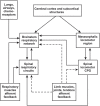
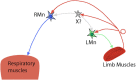
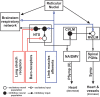
Breathing constantly adapts to environmental, metabolic or behavioral changes by responding to different sensory information, including afferent feedback from muscles. Importantly, not just respiratory muscle feedback influences respiratory activity. Afferent sensory information from rhythmically moving limbs has also been shown to play an essential role in the breathing. The present review will discuss the neuronal mechanisms of respiratory modulation by activation of peripheral muscles that usually occurs during locomotion or exercise. An understanding of these mechanisms and finding the most effective approaches to regulate respiratory motor output by stimulation of limb muscles could be extremely beneficial for people with respiratory dysfunctions. Specific attention in the present review is given to the muscle stimulation to treat respiratory deficits following cervical spinal cord injury.
Keywords: exercise; muscle afferents; muscle stimulation; respiration; spinal cord injury.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bimodal Respiratory-Locomotor Neurons in the Neonatal Rat Spinal Cord.J Neurosci. 2016 Jan 20;36(3):926-37. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1825-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26791221 Free PMC article.
-
On the reflex mechanisms of cervical transcutaneous spinal cord stimulation in human subjects.J Neurophysiol. 2019 May 1;121(5):1672-1679. doi: 10.1152/jn.00802.2018. Epub 2019 Mar 6. J Neurophysiol. 2019. PMID: 30840527
-
Effects from fine muscle and cutaneous afferents on spinal locomotion in cats.J Physiol. 1981;319:543-54. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013925. J Physiol. 1981. PMID: 7320927 Free PMC article.
-
Control of exercise hyperpnoea: Contributions from thin-fibre skeletal muscle afferents.Exp Physiol. 2019 Nov;104(11):1605-1621. doi: 10.1113/EP087649. Epub 2019 Oct 6. Exp Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31429500 Review.
-
Role of Propriospinal Neurons in Control of Respiratory Muscles and Recovery of Breathing Following Injury.Front Syst Neurosci. 2020 Jan 17;13:84. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2019.00084. eCollection 2019. Front Syst Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32009911 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Respiratory function and breathing response to water- and land-based cycling at the matched oxygen uptake.Physiol Rep. 2022 Sep;10(18):e15475. doi: 10.14814/phy2.15475. Physiol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36117322 Free PMC article.
-
Dyspnea in Post-COVID Syndrome following Mild Acute COVID-19 Infections: Potential Causes and Consequences for a Therapeutic Approach.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Mar 12;58(3):419. doi: 10.3390/medicina58030419. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35334595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An attempt to explain the neurological symptoms of Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome.J Transl Med. 2021 Nov 22;19(1):471. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-03143-3. J Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34809664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting apneic events in preterm infants using cardio-respiratory and movement features.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021 Sep;209:106321. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106321. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021. PMID: 34380078 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of aerobic exercise training on muscle plasticity in a mouse model of cervical spinal cord injury.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 8;11(1):112. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80478-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33420246 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abu-Khaber H. A., Abouelela A. M. Z., Abdelkarim E. M. (2013). Effect of electrical muscle stimulation on prevention of ICU acquired muscle weakness and facilitating weaning from mechanical ventilation. Alexandria J. Med. 49 309–315. 10.1016/j.ajme.2013.03.011 - DOI
-
- Amann M., Blain G. M., Proctor L. T., Sebranek J. J., Pegelow D. F., Dempsey J. A. (2010). Group III and IV muscle afferents contribute to ventilatory and cardiovascular response to rhythmic exercise in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 109 966–976. 10.1152/japplphysiol.00462.2010 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Armstrong R. B., Laughlin M. H. (1985). Metabolic indicators of fibre recruitment in mammalian muscles during locomotion. J. Exp. Biol. 115 201–213. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

