The Medicinal Plant Pair Bupleurum chinense- Scutellaria baicalensis - Metabolomics and Metallomics Analysis in a Model for Alcoholic Liver Injury
- PMID: 30971921
- PMCID: PMC6445227
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00254
The Medicinal Plant Pair Bupleurum chinense- Scutellaria baicalensis - Metabolomics and Metallomics Analysis in a Model for Alcoholic Liver Injury
Abstract
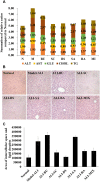
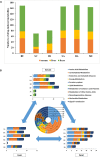
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), a complex natural herbal medicine system, has increasingly attracted attention from all over the world. Most research has illustrated the mechanism of TCM based on the active components or single herbs. It was fruitful and effective but far from satisfactory as it failed to gain insights into the interactivity and combined effects of TCM. In this work, we used Bupleurum chinense (B. chinense DC, a species in the genus Bupleurum, family Apiaceae) and Scutellaria baicalensis (S. baicalensis Georgi, a species in the genus Scutellaria, family Lamiaceae), an herbal pair in TCM, to illustrate the combined effect. We compared the diverse effects between the B. chinense-S. baicalensis herbal pair and its compositions in an animal model of Alcoholic Liver Injury to highlight the advantages of the formula. Biochemical and histological indicators revealed that the effect of B. chinense-S. baicalensis was better than its individual parts. Furthermore, metabolite profiling of the serum, liver tissue, and feces were conducted to reveal that the herbal pair largely presented its effects through enhanced tissue penetration to maintain liver-located intervention with less global and symbiotic disturbance. Furthermore, we analyzed the distribution of the metal elements in extracts of the serum and liver tissue and found that the herbal pair significantly regulated the distribution of endogenous selenium in liver tissue. As selenium plays an important role in the anti-oxidative and hepatoprotective effects, it may be the reason for combined effects in BS formula. This research could open new perspectives for exploring the material basis of combined effects in natural herbal medicine.
Keywords: Bupleurum chinense-Scutellaria baicalensis; alcoholic liver injury; herbal pair; metabolomics; metallomics.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Homotherapy-for-heteropathy of Bupleurum Chinense DC.-Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi in treating depression and colorectal cancer: A network pharmacology and animal model approach.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jun 28;328:118038. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118038. Epub 2024 Mar 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38479544
-
Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. (Lamiaceae): a review of its traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2019 Sep;71(9):1353-1369. doi: 10.1111/jphp.13129. Epub 2019 Jun 24. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31236960 Review.
-
Integrated network pharmacology and metabolomics to dissect the combination mechanisms of Bupleurum chinense DC-Paeonia lactiflora Pall herb pair for treating depression.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Jan 10;264:113281. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113281. Epub 2020 Aug 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32810624
-
Characterizing the Neuroprotective Effects of S/B Remedy (Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi and Bupleurum scorzonerifolfium Willd) in Spinal Cord Injury.Molecules. 2019 May 16;24(10):1885. doi: 10.3390/molecules24101885. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31100896 Free PMC article.
-
Toxic polyacetylenes in the genus Bupleurum (Apiaceae) - Distribution, toxicity, molecular mechanism and analysis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Dec 4;193:566-573. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.09.052. Epub 2016 Sep 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27693772 Review.
Cited by
-
Baicalein Prevents Fructose-Induced Hepatic Steatosis in Rats: In the Regulation of Fatty Acid De Novo Synthesis, Fatty Acid Elongation and Fatty Acid Oxidation.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 30;13:917329. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.917329. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35847050 Free PMC article.
-
The Structural Characteristics of an Acidic Water-Soluble Polysaccharide from Bupleurum chinense DC and Its In Vivo Anti-Tumor Activity on H22 Tumor-Bearing Mice.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Mar 11;14(6):1119. doi: 10.3390/polym14061119. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35335457 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome-Level Genome Assembly of Bupleurum chinense DC Provides Insights Into the Saikosaponin Biosynthesis.Front Genet. 2022 Mar 31;13:878431. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.878431. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35432473 Free PMC article.
-
Kaempferol: Antimicrobial Properties, Sources, Clinical, and Traditional Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 30;23(23):15054. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315054. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499380 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cao G., Li Q., Cai H., Tu S., Cai B. (2014). Investigation of the chemical changes from crude and processed paeoniae radix alba-atractylodis macrocephalae rhizoma herbal pair extracts by using Q exactive high-performance benchtop quadrupole-orbitrap LC-MS/MS. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2014:170959. 10.1155/2014/170959 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carlson B. A., Moustafa M. E., Sengupta A., Schweizer U., Shrimali R., Rao M., et al. (2007). Selective restoration of the selenoprotein population in a mouse hepatocyte selenoproteinless background with different mutant selenocysteine tRNAs lacking Um34. J. Biol. Chem. 282 32591–32602. 10.1074/jbc.M707036200 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

