Treatment With the Delta Opioid Agonist UFP-512 Alleviates Chronic Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain: Mechanisms Implicated
- PMID: 30971925
- PMCID: PMC6443715
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00283
Treatment With the Delta Opioid Agonist UFP-512 Alleviates Chronic Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain: Mechanisms Implicated
Abstract
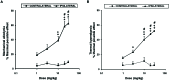
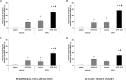
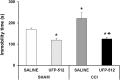
We investigated whether administration of the δ-opioid receptor (DOR) agonist H-Dmt-Tic-NH-CH(CH2-COOH)-Bid (UFP-512), which also activates nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), alleviated chronic inflammatory and/or neuropathic pain and inhibited the depressive-like behaviors associated with persistent neuropathic pain. The possible mechanisms implicated were also assessed. We evaluated the following effects in male C57BL/6J mice with inflammatory pain induced by complete Freund's adjuvant or neuropathic pain caused by the chronic constriction of sciatic nerve: (1) the antinociceptive effects of UFP-512; (2) the effects of UFP-512 on the expression of Nrf2, heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1), NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase 1, phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), protein kinase B (Akt), inducible nitric oxide synthase, DOR, and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) in the spinal cord of animals with inflammatory or neuropathic pain; (3) the antinociceptive effects of the coadministration of UFP-512 with the Nrf2 activator sulforaphane (SFN); and (4) the antidepressant effects of UFP-512 in animals with depressive-like behaviors associated with neuropathic pain. Our results demonstrated that the intraperitoneal administration of UFP-512 inhibited chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain and reduced the depressive-like behaviors associated with persistent neuropathic pain. The antiallodynic effects of UFP-512 were significantly augmented when it was coadministered with SFN in both types of chronic pain. The administration of UFP-512 increased/reestablished the spinal cord protein levels of Nrf2 and HO-1 in mice with inflammatory or neuropathic pain. However, while during inflammatory pain UFP-512 inhibited spinal c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and extracellular signal regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) phosphorylation induced by peripheral inflammation. This DOR agonist blocked the spinal activated PI3K/Akt signaling pathway under chronic neuropathic pain conditions, but it did not alter the enhanced protein levels of p-JNK or p-ERK1/2 induced by sciatic nerve injury. These results revealed the antinociceptive and antidepressant effects of UFP-512 in animals with chronic pain and the different mechanism of action of this DOR agonist in the presence of inflammatory or neuropathic pain. Our data also suggest the administration of UFP-512 as an alternative for the treatment of chronic pain and the depressive-like behaviors associated with neuropathic pain.
Keywords: Nrf2 transcription factor; UFP-512; analgesia; chronic pain; delta opioid receptors; depression; oxidative stress.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Sulforaphane Inhibited the Nociceptive Responses, Anxiety- and Depressive-Like Behaviors Associated With Neuropathic Pain and Improved the Anti-allodynic Effects of Morphine in Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Nov 20;9:1332. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01332. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30542282 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment with Sulforaphane Produces Antinociception and Improves Morphine Effects during Inflammatory Pain in Mice.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2017 Dec;363(3):293-302. doi: 10.1124/jpet.117.244376. Epub 2017 Sep 25. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2017. PMID: 28947488
-
Mechanism implicated in the anti-allodynic and anti-hyperalgesic effects induced by the activation of heme oxygenase 1/carbon monoxide signaling pathway in the central nervous system of mice with neuropathic pain.Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Feb;148:52-63. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.12.007. Epub 2017 Dec 13. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29247614
-
The role of carbon monoxide, heme oxygenase 1, and the Nrf2 transcription factor in the modulation of chronic pain and their interactions with opioids and cannabinoids.Med Res Rev. 2021 Jan;41(1):136-155. doi: 10.1002/med.21726. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Med Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 32820550 Review.
-
Opioids in chronic pain.Eur J Pharmacol. 2001 Oct 19;429(1-3):79-91. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(01)01308-5. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11698029 Review.
Cited by
-
δ-Opioid Receptor Activation Inhibits Ferroptosis by Activating the Nrf2 Pathway in MPTP-Induced Parkinson Disease Models.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Feb 10;2023:4130937. doi: 10.1155/2023/4130937. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 36818224 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating β-arrestin 2 recruitment at the δ- and μ-opioid receptors using peptidomimetic ligands.RSC Med Chem. 2021 Aug 16;12(11):1958-1967. doi: 10.1039/d1md00025j. eCollection 2021 Nov 17. RSC Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34825191 Free PMC article.
-
δ-opioid Receptor, Microglia and Neuroinflammation.Aging Dis. 2023 Jun 1;14(3):778-793. doi: 10.14336/AD.2022.0912. Aging Dis. 2023. PMID: 37191426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogen Sulfide Inhibits Inflammatory Pain and Enhances the Analgesic Properties of Delta Opioid Receptors.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Dec 11;10(12):1977. doi: 10.3390/antiox10121977. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943080 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and Pharmacological Blockade of Sigma-1 Receptors Attenuates Inflammation-Associated Hypersensitivity during Acute Colitis in CD1 Mice.Biomedicines. 2023 Oct 12;11(10):2758. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102758. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37893131 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguila B., Coulbault L., Boulouard M., Léveillé F., Davis A., Tóth G., et al. (2007). In vitro and in vivo pharmacological profile of UFP-512, a novel selective delta-opioid receptor agonist; correlations between desensitization and tolerance. Br. J. Pharmacol. 152 1312–1324. 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707497 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Albert-Vartanian A., Boyd M. R., Hall A. L., Morgado S. J., Nguyen E., Nguyen V. P., et al. (2016). Will peripherally restricted kappa-opioid receptor agonists (pKORAs) relieve pain with less opioid adverse effects and abuse potential? J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 41 371–382. 10.1111/jcpt.12404 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

