Comparison Between Movement-Based and Task-Based Mirror Therapies on Improving Upper Limb Functions in Patients With Stroke: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 30972016
- PMCID: PMC6443927
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00288
Comparison Between Movement-Based and Task-Based Mirror Therapies on Improving Upper Limb Functions in Patients With Stroke: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
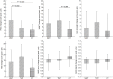
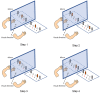
Objective: The aim of this trial was to compare the effect of movement-based mirror therapy (MMT) and task-based mirror therapy (TMT) on improving upper limb functions in patients with stroke. Methods: A total of 34 patients with sub-acute stroke with mildly to moderately impaired upper limb motor functions. The participants were randomly allocated to one of three groups: MMT, TMT, and conventional treatment (CT). The MMT group underwent movement-based mirror therapy for around 30 min/day, 5 days/week, for 4 weeks, whereas the TMT group underwent dose-matched TMT. The CT group underwent only conventional rehabilitation. The MMT and TMT groups underwent CT in addition to their mirror therapy. Blinded assessments were administered at baseline and immediately after the intervention. Upper limb motor functions, measured using Fugl-Meyer Assessment-upper extremity (FMA-UE), Wolf Motor Function Test (WMFT), and hand grip strength; upper limb spasticity, measured using the modified Ashworth scale (MAS); and activities of daily living, measured using the modified Barthel index (MBI). Results: A significant time-by-group interaction effect was noted in FMA-UE. Post-hoc analysis of change scores showed that MMT yielded a better effect on improving FMA-UE than the other two therapies, at a marginally significant level (P = 0.050 and 0.022, respectively). No significant interaction effect was noted in WMFT, hand grip strength, MAS, and MBI. Conclusion: Both MMT and TMT are effective in improving the upper limb function of patients with mild to moderate hemiplegia due to stroke. Nevertheless, MMT seems to be superior to TMT in improving hemiplegic upper extremity impairment. Further studies with larger stroke cohorts are expected to be inspired by this pilot trial. Trial registration number: No. ChiCTR1800019043 (http://www.chictr.org.cn/index.aspx).
Keywords: mirror therapy; rehabilitation; stroke; task-oriented training; upper limb.
Figures

References
-
- Shih TY, Wu CY, Lin KC, Cheng CH, Hsieh YW, Chen CL, et al. . Effects of action observation therapy and mirror therapy after stroke on rehabilitation outcomes and neural mechanisms by MEG: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. (2017) 18:459. 10.1186/s13063-017-2205-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

