Ulnar Neuropathy at the Elbow Associated With Focal Demyelination in the Proximal Forearm and Intraoperative Imaging Correlation
- PMID: 30972017
- PMCID: PMC6445876
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00292
Ulnar Neuropathy at the Elbow Associated With Focal Demyelination in the Proximal Forearm and Intraoperative Imaging Correlation
Abstract
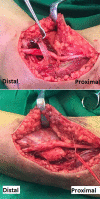
Ulnar nerve focal demyelination (FD) in the forearm [defined as conduction block (CB) and or temporal dispersion (TD)] has been described with immune-mediated neuropathy and with compression affecting the forearm segment of the nerve. The association of FD in the forearm with entrapment ulnar neuropathy at the elbow, as well as the intraoperative imaging of the abnormal ulnar nerve at the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle level (FCU), has not been reported before. We report a 33-years-old woman presented with only sensory symptoms of the right hand suggestive of right ulnar neuropathy for the last 10 years. On clinical examination, she had reduced pinprick sensation on the little and ring fingers with no motor deficit. Nerve-conduction study showed slowing of conduction velocity across the elbow on the right when recording at the abductor digiti minimi (ADM) and first dorsal interossei (FDI). There was 63% amplitude drop when stimulating below the elbow compared to distal stimulation at the wrist. Increment inching study localized the block at 5 cm distal to the medial epicondyle. During surgical transposition, the ulnar nerve was swollen, and edematous in the segment where the nerve enters the FCU muscle, which provides a physiological explanation for the electrophysiological findings. After the surgery, the patient reported complete resolution of the symptoms. This case demonstrate that ulnar nerve motor potential FD at the proximal forearm could be recorded and it is still compatible with ulnar-nerve entrapment at the elbow.
Keywords: conduction block; cubital tunnel; entrapment; neuropathy; ulnar.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ulnar Nerve Entrapment.2023 Aug 7. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2023 Aug 7. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 32310389 Free Books & Documents.
-
Ulnar Neuropathy.2023 Aug 13. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2023 Aug 13. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30480959 Free Books & Documents.
-
[Electrophysiological diagnosis in ulnar nerve entrapment at elbow].Nihon Seikeigeka Gakkai Zasshi. 1990 Jan;64(1):7-16. Nihon Seikeigeka Gakkai Zasshi. 1990. PMID: 2319194 Japanese.
-
Ultrasound of the elbow with emphasis on detailed assessment of ligaments, tendons, and nerves.Eur J Radiol. 2015 Apr;84(4):671-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2014.12.007. Epub 2014 Dec 19. Eur J Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25638576 Review.
-
The electrodiagnosis of ulnar nerve entrapment at the elbow.Can J Neurol Sci. 2003 Nov;30(4):314-9. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100003012. Can J Neurol Sci. 2003. PMID: 14672262 Review.
Cited by
-
The red flags of ulnar neuropathy in leprosy.PLoS One. 2021 Nov 19;16(11):e0259804. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259804. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34797866 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Preston DC, Shapiro BE. Electromyography and Neuromuscular Disorders: Clinical-Electrophysiologic Correlations. 3rd ed. London; New York, NY: Elsevier Saunders; (2013).
-
- Practice parameter for electrodiagnostic studies in ulnar neuropathy at the elbow: summary statement American association of electrodiagnostic medicine, American academy of neurology, American academy of physical medicine and rehabilitation. Muscle Nerve. (1999) 22:408–11. 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4598(199903)22:3<408::AID-MUS16>3.0.CO;2-7 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

