Combination effects of baicalin with levofloxacin against biofilm-related infections
- PMID: 30972161
- PMCID: PMC6456525
Combination effects of baicalin with levofloxacin against biofilm-related infections
Abstract
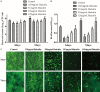
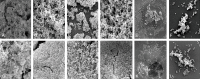
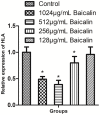
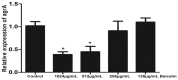
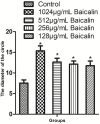
It is important to improve the existing techniques and develop new strategies to prevent bacterial biofilm formation. In this in vitro study, biofilms were established by a clinically isolated strain of Staphylococcus aureus 17546 (t037). Different concentrations of baicalin were added to 3- and 7-day biofilms. Based on colony counts and quantitative analysis of the biomass, sub-minimum inhibitory concentrations (sub-MICs) (1024, 512 or 256 μg/mL) of baicalin clearly decreased the number of bacterial colonies and biomass in vitro. Fluorescence microscopy revealed that sub-MICs (1024, 512, or 256 μg/mL) of baicalin inhibited bacterial adherence to the carrier surface and decreased polysaccharide production. Moreover, baicalin disrupted biofilms and exhibited synergistic effects with levofloxacin. Virulence factors were assessed by western blotting and real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction, confirming that staphylococcal enterotoxin A, α-haemolysin and coagulase production decreased after baicalin treatment. Additionally, baicalin increased production of thermonuclease in S. aureus, and baicalin at 1024 and 512 μg/mL downregulated agrA expression. Based on these findings, the combination of baicalin with levofloxacin might be a new, feasible strategy for treating S. aureus biofilm-related infections. Baicalin may serve as a new inhibitor that modulates S. aureus virulence factors.
Keywords: Biofilm; baicalin; staphylococcus aureus; virulence factors.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures





References
-
- Nickel JC, Gristina AG, Costerton JW. Electron microscopic study of an infected Foley catheter. Can J Surg. 1985;28:50–51. 54. - PubMed
-
- Peters RG, Jones WC, Cromartie TH. Inactivation of L-lactate monooxygenase with 2,3-butanedione and phenylglyoxal. Biochemistry. 1981;20:2564–2571. - PubMed
-
- Tenney JH, Moody MR, Newman KA, Schimpff SC, Wade JC, Costerton JW, Reed WP. Adherent microorganisms on lumenal surfaces of long-term intravenous catheters. Importance of staphylococcus epidermidis in patients with cancer. Arch Intern Med. 1986;146:1949–1954. - PubMed
-
- Parvizi J, Alijanipour P, Barberi EF, Hickok NJ, Phillips KS, Shapiro IM, Schwarz EM, Stevens MH, Wang Y, Shirtliff ME. Novel developments in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of periprosthetic joint infections. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23(Suppl):S32–43. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
