Shank3 modulates sleep and expression of circadian transcription factors
- PMID: 30973326
- PMCID: PMC6488297
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.42819
Shank3 modulates sleep and expression of circadian transcription factors
Abstract
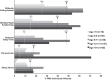
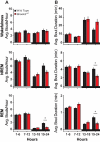
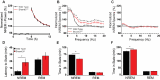
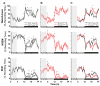
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is the most prevalent neurodevelopmental disorder in the United States and often co-presents with sleep problems. Sleep problems in ASD predict the severity of ASD core diagnostic symptoms and have a considerable impact on the quality of life of caregivers. Little is known, however, about the underlying molecular mechanisms of sleep problems in ASD. We investigated the role of Shank3, a high confidence ASD gene candidate, in sleep architecture and regulation. We show that mice lacking exon 21 of Shank3 have problems falling asleep even when sleepy. Using RNA-seq we show that sleep deprivation increases the differences in prefrontal cortex gene expression between mutants and wild types, downregulating circadian transcription factors Per3, Bhlhe41, Hlf, Tef, and Nr1d1. Shank3 mutants also have trouble regulating wheel-running activity in constant darkness. Overall, our study shows that Shank3 is an important modulator of sleep and clock gene expression.
Keywords: Shank3; autism spectrum disorder; mouse; neuroscience; sleep.
© 2019, Ingiosi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AI, HS, TW, KS, DR, LR, EM, DR, MF, LP No competing interests declared
Figures

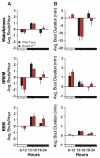
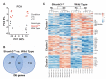
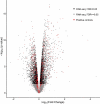
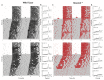
References
-
- Achermann P, Borbely AA. Sleep homeostasis and models of sleep regulation. In: Kryger M, Roth T, Dement W. C, editors. Principles and Practice of Sleep Medicine. 6th Ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2017. pp. 377–387. - DOI
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th Edition. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

