The Common Antidiabetic Drug Metformin Reduces Odds of Developing Age-Related Macular Degeneration
- PMID: 30973575
- PMCID: PMC6736343
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.18-26422
The Common Antidiabetic Drug Metformin Reduces Odds of Developing Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Abstract
Purpose: AMD is the leading cause of irreversible blindness in older individuals in the Western world, and there are currently no therapies to halt disease progression. Studies suggest that the commonly prescribed antidiabetic drug, metformin, is associated with decreased risk of several ocular diseases, but no work has investigated the effect of metformin use on development of AMD. Thus, we aim to investigate whether metformin use is associated with decreased risk of developing AMD.
Methods: In this retrospective case-control study, we used medical records from patients older than 55 who have visited a University of Florida health clinic. Three controls were matched for every AMD case, defined by International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision code, based on the Charlson Comorbidity Index to ensure comparable baseline overall health status. Univariate and conditional multivariable logistic regressions were used to determine the association between a variety of covariates, including metformin use, and AMD diagnosis.
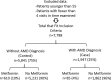
Results: Metformin use was associated with decreased odds of developing AMD, independently of the other covariates investigated, with an odds ratio of 0.58 and a 95% confidence interval of 0.43 to 0.79. Other medications assessed were not associated with decreased odds of developing AMD.
Conclusions: Patients who had taken metformin had decreased odds of developing AMD, suggesting that metformin may have a therapeutic role in AMD development or progression in those who are at risk. Further work should include clinical trials to investigate prospectively whether metformin has a protective effect in those at risk for developing AMD.
Figures
References
-
- Leibowitz HM, Krueger DE, Maunder LR, et al. The Framingham Eye Study monograph: an ophthalmological and epidemiological study of cataract, glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, macular degeneration, and visual acuity in a general population of 2631 adults, 1973–1975. Surv Ophthalmol. 1980;24(suppl):335–610. - PubMed
-
- Lim JY, Lee SY, Kim JG, Lee JY, Chung H, Yoon YH. Intravitreal bevacizumab alone versus in combination with photodynamic therapy for the treatment of neovascular maculopathy in patients aged 50 years or older: 1-year results of a prospective clinical study. Acta Ophthalmol. 2012;90:61–67. - PubMed
-
- Malgorzata F. Effectivity and safety of bevacizumab intravitreal injections for exudative age-related macular degeneration treatment--6 months observations. Klin Oczna. 2010;112:213–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical