High SRC-1 and Twist1 expression predicts poor prognosis and promotes migration and invasion by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PMID: 30973923
- PMCID: PMC6459498
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215299
High SRC-1 and Twist1 expression predicts poor prognosis and promotes migration and invasion by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Abstract
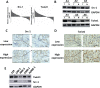
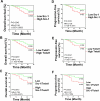
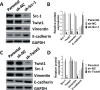
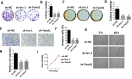
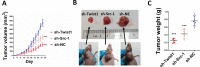
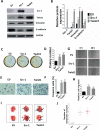
Steroid receptor coactivator 1 (Src-1) and Twist1 are aberrantly upregulated in a variety of tumors and play an important role in tumor progression. However, the exact role of Src-1 and Twist1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is uncertain. In this study, we investigated the possible prognostic value and biological effect of Src-1 and Twist1 in NPC. Src-1 and Twist1 expression was detected in a cohort of NPC patients (n = 134) by qRT-PCR. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was used comparing overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS). Multivariate analysis was performed using the Cox proportional hazard regression model. Biologic effect of Src-1 and Twist1 in NPC cell lines was evaluated by western blot, colony formation assay, soft agar assay, scratch wound healing assay, transwell invasion assay and tumor xenografts growth. We have found that Src-1 and Twist1 were aberrantly upregulated in human NPC tissues, and associated with advanced tumor stage, distant metastasis and unfavorable prognosis. Knockdown of Src-1 or Twist1 in human NPC cell line CNE-1 suppressed colony formation, anchorage-independent growth, cell migration, invasion and tumor xenografts growth, while enforced expression of Src-1 or Twist1 in human NPC cell line HNE-2 promotes anchorage-independent growth, cell migration and invasion. In addition, Src-1 and Twist1 could suppress E-cadherin expression and increase Vimentin expression, thus suggested that Src-1 and Twist1 enhanced the malignant behaviors of NPC cells via inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Our data indicated that Src-1 and Twist1 could be possible prognostic biomarkers and potential therapy targets for patients with NPC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
c-Src activation promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis by inducing the epithelial-mesenchymal transition via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway: a new and promising target for NPC.Oncotarget. 2016 May 10;7(19):28340-55. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8634. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27078847 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of long non-coding RNA TUG1 suppresses nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) via the promotion of miR-384.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019 Jan 29;509(1):56-63. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.12.011. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019. PMID: 30581000
-
Downregulating HMGA2 attenuates epithelial-mesenchymal transition-induced invasion and migration in nasopharyngeal cancer cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Jul 31;463(3):357-63. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.05.068. Epub 2015 May 27. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 26025649
-
Normal and disease-related biological functions of Twist1 and underlying molecular mechanisms.Cell Res. 2012 Jan;22(1):90-106. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.144. Epub 2011 Aug 30. Cell Res. 2012. PMID: 21876555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research status and prospects of biomarkers for nasopharyngeal carcinoma in the era of high‑throughput omics (Review).Int J Oncol. 2021 Apr;58(4):9. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2021.5188. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Int J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33649830 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Src-1 and SP2 promote the proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Open Med (Wars). 2021 Jul 15;16(1):1061-1069. doi: 10.1515/med-2021-0248. eCollection 2021. Open Med (Wars). 2021. PMID: 34307888 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-conditioned Medium Protecting Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells by Inhibiting Hypoxia-inducible Factor-1α and Nuclear Receptor Coactivator-1.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024;19(10):1369-1381. doi: 10.2174/011574888X247652230928064627. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 37817516
-
NF-κB/TWIST1 Mediates Migration and Phagocytosis of Macrophages in the Mice Model of Implant-Associated Staphylococcus aureus Osteomyelitis.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jun 12;11:1301. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01301. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32595631 Free PMC article.
-
Contrast-enhanced Ultrasound in evaluating of angiogenesis and tumor staging of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in nude mice.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 23;14(8):e0221638. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221638. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31442259 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yu MC, Yuan JM. Epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Seminars in cancer biology. 2002;12(6):421–9. . - PubMed
-
- Andersson-Anvret M, Forsby N, Klein G, Henle W. Relationship between the Epstein-Barr virus and undifferentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma: correlated nucleic acid hybridization and histopathological examination. International journal of cancer. 1977;20(4):486–94. . - PubMed
-
- Ward MH, Pan WH, Cheng YJ, Li FH, Brinton LA, Chen CJ, et al. Dietary exposure to nitrite and nitrosamines and risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Taiwan. International journal of cancer. 2000;86(5):603–9. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

