Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Effects of Peptides from Venom of Social Wasp and Scorpion on Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
- PMID: 30974767
- PMCID: PMC6520840
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins11040216
Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Effects of Peptides from Venom of Social Wasp and Scorpion on Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
Abstract
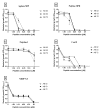
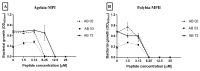
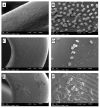
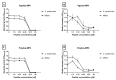
Intravascular stent infection is a rare complication with a high morbidity and high mortality; bacteria from the hospital environment form biofilms and are often multidrug-resistant (MDR). Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) have been considered as alternatives to bacterial infection treatment. We analyzed the formation of the bacterial biofilm on the vascular stents and also tested the inhibition of this biofilm by AMPs to be used as treatment or coating. Antimicrobial activity and antibiofilm were tested with wasp (Agelaia-MPI, Polybia-MPII, Polydim-I) and scorpion (Con10 and NDBP5.8) AMPs against Acinetobacter baumannii clinical strains. A. baumannii formed a biofilm on the vascular stent. Agelaia-MPI and Polybia-MPII inhibited biofilm formation with bacterial cell wall degradation. Coating biofilms with polyethylene glycol (PEG 400) and Agelaia-MPI reduced 90% of A. baumannii adhesion on stents. The wasp AMPs Agelaia-MPI and Polybia-MPII had better action against MDR A. baumannii adherence and biofilm formation on vascular stents, preventing its formation and treating mature biofilm when compared to the other tested peptides.
Keywords: AMP; Acinetobacter baumannii; mastoparan; stent.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Synergistic effects and antibiofilm properties of chimeric peptides against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii strains.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(3):1622-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02473-13. Epub 2013 Dec 23. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24366740 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial peptides as a promising treatment option against Acinetobacter baumannii infections.Microb Pathog. 2020 Sep;146:104238. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104238. Epub 2020 May 5. Microb Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32387392 Review.
-
Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Peptide Octominin for Controlling Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 19;22(10):5353. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105353. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34069596 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro activity of several antimicrobial peptides against colistin-susceptible and colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012 Apr;18(4):383-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03581.x. Epub 2011 Jun 14. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012. PMID: 21672084
-
Wasp Venom: Future Breakthrough in Production of Antimicrobial Peptides.Protein J. 2025 Feb;44(1):35-47. doi: 10.1007/s10930-024-10242-9. Epub 2024 Dec 4. Protein J. 2025. PMID: 39633224 Review.
Cited by
-
Mastoparans: A Group of Multifunctional α-Helical Peptides With Promising Therapeutic Properties.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Jun 24;9:824989. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.824989. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35813822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arthropod Venom Components and Their Potential Usage.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Jan 25;12(2):82. doi: 10.3390/toxins12020082. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31991714 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Synthetic Peptide Agelaia-12 Has Improved Activity Against Mycobacterium abscessus Complex.Pathogens. 2024 Nov 13;13(11):994. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13110994. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39599547 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic Insight into the Early Stages of Toroidal Pore Formation by the Antimicrobial Peptide Smp24.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Sep 28;15(10):2399. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15102399. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37896158 Free PMC article.
-
Mass spectrometry-based top-down and bottom-up approaches for proteomic analysis of the Moroccan Buthus occitanus scorpion venom.FEBS Open Bio. 2021 Jul;11(7):1867-1892. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13143. Epub 2021 May 28. FEBS Open Bio. 2021. PMID: 33715301 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Minardi D., Ghiselli R., Cirioni O., Giacometti A., Kamysz W., Orlando F., Silvestri C., Parri G., Kamysz E., Scalise G., et al. The antimicrobial peptide Tachyplesin III coated alone and in combination with intraperitoneal piperacillin-tazobactam prevents ureteral stent Pseudomonas infection in a rat subcutaneous pouch model. Peptides. 2007;28:2293–2298. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2007.10.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- De Breij A., Riool M., Kwakman P.H.S., de Boer L., Cordfunke R.A., Drijfhout J.W., Cohen O., Emanuel N., Zaat S.A.J., Nibbering P.H., et al. Prevention of Staphylococcus aureus biomaterial-associated infections using a polymer-lipid coating containing the antimicrobial peptide OP-145. J. Control. Release. 2016;222:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.12.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dalal J.J., Digrajkar A., Hastak M., Mulay A., Lad V., Wani S. Coronary stent infection—A grave, avoidable complication. IHJ Cardiovasc. Case Rep. 2017;1:77–79. doi: 10.1016/j.ihjccr.2017.07.002. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

