Long Term Outcomes and Effects of Surgery on Degenerative Spinal Deformity: A 14-Year National Cohort Study
- PMID: 30974773
- PMCID: PMC6518357
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm8040483
Long Term Outcomes and Effects of Surgery on Degenerative Spinal Deformity: A 14-Year National Cohort Study
Abstract
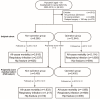
Degenerative spinal deformity (DSD) has become a prevalent cause of disability and pain among the aging population worldwide. Though surgery has emerged as a promising option for DSD, the natural course, outcomes, and effects of surgery on DSD have remained elusive. This cohort study used a national database to comprehensively follow up patients of DSD for all-cause mortality, respiratory problems, and hip fracture-related hospitalizations. All patients were grouped into an operation or a non-operation group for comparison. An adjustment of demographics, comorbidities, and propensity-score matching was conducted to ameliorate confounders. A Cox regression hazard ratio (HR) model and Kaplan-Meier analysis were also applied. The study comprised 21,810 DSD patients, including 12,544 of the operation group and 9266 of the non-operation group. During the 14 years (total 109,591.2 person-years) of follow-up, the operation group had lower mortality (crude hazard ratio = 0.40), lower respiratory problems (cHR = 0.45), and lower hip fractures (cHR = 0.63) than the non-operation group (all p < 0.001). After adjustment, the risks for mortality and respiratory problems remained lower (adjusted HR = 0.60 and 0.65, both p < 0.001) in the operation than the non-operation group, while hip fractures were indifferent (aHR = 1.08, p > 0.05). Therefore, surgery for DSD is invaluable since it could reduce the risks of mortality and of hospitalization for respiratory problems.
Keywords: Degenerative Spinal Deformity (DSD); hip fractures; mortality; respiratory problems; surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Xu L., Sun X., Huang S., Zhu Z., Qiao J., Zhu F., Mao S., Ding Y., Qiu Y. Degenerative lumbar scoliosis in Chinese Han population: Prevalence and relationship to age, gender, bone mineral density, and body mass index. Eur. Spine J. 2013;22:1326–1331. doi: 10.1007/s00586-013-2678-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

