Diverse Role of SNARE Protein Sec22 in Vesicle Trafficking, Membrane Fusion, and Autophagy
- PMID: 30974782
- PMCID: PMC6523435
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8040337
Diverse Role of SNARE Protein Sec22 in Vesicle Trafficking, Membrane Fusion, and Autophagy
Abstract
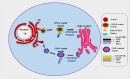
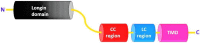
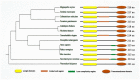
Protein synthesis begins at free ribosomes or ribosomes attached with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Newly synthesized proteins are transported to the plasma membrane for secretion through conventional or unconventional pathways. In conventional protein secretion, proteins are transported from the ER lumen to Golgi lumen and through various other compartments to be secreted at the plasma membrane, while unconventional protein secretion bypasses the Golgi apparatus. Soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptors (SNARE) proteins are involved in cargo vesicle trafficking and membrane fusion. The ER localized vesicle associated SNARE (v-SNARE) protein Sec22 plays a major role during anterograde and retrograde transport by promoting efficient membrane fusion and assisting in the assembly of higher order complexes by homodimer formation. Sec22 is not only confined to ER-Golgi intermediate compartments (ERGIC) but also facilitates formation of contact sites between ER and plasma membranes. Sec22 mutation is responsible for the development of atherosclerosis and symptoms in the brain in Alzheimer's disease and aging in humans. In the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster, Sec22 is essential for photoreceptor morphogenesis, the wingless signaling pathway, and normal ER, Golgi, and endosome morphology. In the plant Arabidopsis thaliana, it is involved in development, and in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, it is in involved in the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway. In filamentous fungi, it affects cell wall integrity, growth, reproduction, pathogenicity, regulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), expression of extracellular enzymes, and transcriptional regulation of many development related genes. This review provides a detailed account of Sec22 function, summarizes its domain structure, discusses its genetic redundancy with Ykt6, discusses what is known about its localization to discrete membranes, its contributions in conventional and unconventional autophagy, and a variety of other roles across different cellular systems ranging from higher to lower eukaryotes, and highlights some of the surprises that have originated from research on Sec22.
Keywords: ER; ERGIC; Golgi; Sec22; autophagy; vesicle trafficking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The authors declare that the research is being conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

