Two Component Regulatory Systems and Antibiotic Resistance in Gram-Negative Pathogens
- PMID: 30974906
- PMCID: PMC6480566
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20071781
Two Component Regulatory Systems and Antibiotic Resistance in Gram-Negative Pathogens
Abstract
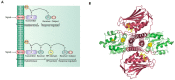
Gram-negative pathogens such as Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa are the leading cause of nosocomial infections throughout the world. One commonality shared among these pathogens is their ubiquitous presence, robust host-colonization and most importantly, resistance to antibiotics. A significant number of two-component systems (TCSs) exist in these pathogens, which are involved in regulation of gene expression in response to environmental signals such as antibiotic exposure. While the development of antimicrobial resistance is a complex phenomenon, it has been shown that TCSs are involved in sensing antibiotics and regulating genes associated with antibiotic resistance. In this review, we aim to interpret current knowledge about the signaling mechanisms of TCSs in these three pathogenic bacteria. We further attempt to answer questions about the role of TCSs in antimicrobial resistance. We will also briefly discuss how specific two-component systems present in K. pneumoniae, A. baumannii, and P. aeruginosa may serve as potential therapeutic targets.
Keywords: antimicrobial resistance; biofilms; two-component regulatory proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- World Health Organization . Prioritization of Pathogens to Guide Discovery, Research and Development of New Antibiotics for Drug-Resistant Bacterial Infections, Including Tuberculosis. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2017. p. 12.
-
- Chairat S., Ben Yahia H., Rojo-Bezares B., Saenz Y., Torres C., Ben Slama K. High prevalence of imipenem-resistant and metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the Burns Hospital in Tunisia: Detection of a novel class 1 integron. J. Chemother. 2019:1–7. doi: 10.1080/1120009X.2019.1582168. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

