Derivation of adult canine intestinal organoids for translational research in gastroenterology
- PMID: 30975131
- PMCID: PMC6460554
- DOI: 10.1186/s12915-019-0652-6
Derivation of adult canine intestinal organoids for translational research in gastroenterology
Abstract
Background: Large animal models, such as the dog, are increasingly being used for studying diseases including gastrointestinal (GI) disorders. Dogs share similar environmental, genomic, anatomical, and intestinal physiologic features with humans. To bridge the gap between commonly used animal models, such as rodents, and humans, and expand the translational potential of the dog model, we developed a three-dimensional (3D) canine GI organoid (enteroid and colonoid) system. Organoids have recently gained interest in translational research as this model system better recapitulates the physiological and molecular features of the tissue environment in comparison with two-dimensional cultures.
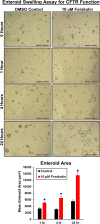
Results: Organoids were derived from tissue of more than 40 healthy dogs and dogs with GI conditions, including inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and intestinal carcinomas. Adult intestinal stem cells (ISC) were isolated from whole jejunal tissue as well as endoscopically obtained duodenal, ileal, and colonic biopsy samples using an optimized culture protocol. Intestinal organoids were comprehensively characterized using histology, immunohistochemistry, RNA in situ hybridization, and transmission electron microscopy, to determine the extent to which they recapitulated the in vivo tissue characteristics. Physiological relevance of the enteroid system was defined using functional assays such as optical metabolic imaging (OMI), the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) function assay, and Exosome-Like Vesicles (EV) uptake assay, as a basis for wider applications of this technology in basic, preclinical and translational GI research. We have furthermore created a collection of cryopreserved organoids to facilitate future research.
Conclusions: We establish the canine GI organoid systems as a model to study naturally occurring intestinal diseases in dogs and humans, and that can be used for toxicology studies, for analysis of host-pathogen interactions, and for other translational applications.
Keywords: Canine; Enteroid; GI diseases; Intestinal stem cell; Organoid model; Translational research.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ information
Not applicable
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All animal studies were reviewed and approved by Iowa State University IACUC, as detailed in the Methods.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
JPM, KA, and AJ would like to disclose a competing financial interest and management role in 3D Health Solutions, Inc., an entity that provides canine 3D organoid testing services. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures








References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

