Inherited predisposition to malignant mesothelioma and overall survival following platinum chemotherapy
- PMID: 30975761
- PMCID: PMC6500142
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1821510116
Inherited predisposition to malignant mesothelioma and overall survival following platinum chemotherapy
Abstract
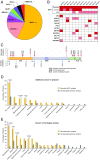
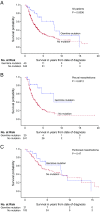
Survival from malignant mesothelioma, particularly pleural mesothelioma, is very poor. For patients with breast, ovarian, or prostate cancers, overall survival is associated with increased sensitivity to platinum chemotherapy due to loss-of-function mutations in DNA repair genes. The goal of this project was to evaluate, in patients with malignant mesothelioma, the relationship between inherited loss-of-function mutations in DNA repair and other tumor suppressor genes and overall survival following platinum chemotherapy. Patients with histologically confirmed malignant mesothelioma were evaluated for inherited mutations in tumor suppressor genes. Survival was evaluated with respect to genotype and site of mesothelioma. Among 385 patients treated with platinum chemotherapy, median overall survival was significantly longer for patients with loss-of-function mutations in any of the targeted genes compared with patients with no such mutation (P = 0.0006). The effect of genotype was highly significant for patients with pleural mesothelioma (median survival 7.9 y versus 2.4 y, P = 0.0012), but not for patients with peritoneal mesothelioma (median survival 8.2 y versus 5.4 y, P = 0.47). Effect of patient genotype on overall survival, measured at 3 y, remained independently significant after adjusting for gender and age at diagnosis, two other known prognostic factors. Patients with pleural mesothelioma with inherited mutations in DNA repair and other tumor suppressor genes appear to particularly benefit from platinum chemotherapy compared with patients without inherited mutations. These patients may also benefit from other DNA repair targeted therapies such as poly-ADP ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitors.
Keywords: BAP1; DNA repair genes; inherited genetics; mesothelioma; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: R.H. has received funding for conduct of clinical trials via a cooperative agreement between NCI and Bayer AG, Aduro BioTech, and Morphotek Inc. H.L.K. has consulting relationships with Aduro Biotech, MedImmune, Bayer, Celgene, GlaxoSmithKline, AstraZeneca, Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Ipsen, Erytech Pharma, Five Prime Therapeutics, and Paredox Therapeutics. J.E.C. received a pilot research grant from the University of Chicago Comprehensive Cancer Center, which was supported with funds from the law firm of Cooney and Conway.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

