Comparison of Major Protein-Source Foods and Other Food Groups in Meat-Eaters and Non-Meat-Eaters in the EPIC-Oxford Cohort
- PMID: 30979052
- PMCID: PMC6521004
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11040824
Comparison of Major Protein-Source Foods and Other Food Groups in Meat-Eaters and Non-Meat-Eaters in the EPIC-Oxford Cohort
Abstract
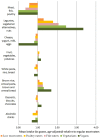
Differences in health outcomes between meat-eaters and non-meat-eaters might relate to differences in dietary intakes between these diet groups. We assessed intakes of major protein-source foods and other food groups in six groups of meat-eaters and non-meat-eaters participating in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC)-Oxford study. The data were from 30,239 participants who answered questions regarding their consumption of meat, fish, dairy or eggs and completed a food frequency questionnaire (FFQ) in 2010. Participants were categorized as regular meat-eaters, low meat-eaters, poultry-eaters, fish-eaters, vegetarians and vegans. FFQ foods were categorized into 45 food groups and analysis of variance was used to test for differences between age-adjusted mean intakes of each food group by diet group. Regular meat-eaters, vegetarians and vegans, respectively, consumed about a third, quarter and a fifth of their total energy intake from high protein-source foods. Compared with regular meat-eaters, low and non-meat-eaters consumed higher amounts of high-protein meat alternatives (soy, legumes, pulses, nuts, seeds) and other plant-based foods (whole grains, vegetables, fruits) and lower amounts of refined grains, fried foods, alcohol and sugar-sweetened beverages. These findings provide insight into potential nutritional explanations for differences in health outcomes between diet groups.
Keywords: cohort; diet; food intake; low-meat; vegans; vegetarians.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Crowe F.L., Appleby P.N., Allen N.E., Key T.J. Diet and risk of diverticular disease in Oxford cohort of European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC): Prospective study of British vegetarians and non-vegetarians. BMJ. 2011;343:d4131. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d4131. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

