Drug Delivery Systems Obtained from Silica Based Organic-Inorganic Hybrids
- PMID: 30979199
- PMCID: PMC6432574
- DOI: 10.3390/polym8040091
Drug Delivery Systems Obtained from Silica Based Organic-Inorganic Hybrids
Abstract
This is a review of hybrid materials based on silica as an inorganic phase used as drug delivery systems (DDS). Silica based DDS have shown effectivity when compared with traditional delivery systems. They present advantages such as: (a) ability to maintain the therapeutic range with minor variations; (b) prevention of local and systemic toxic effects; (c) plasma concentrations increase of substances with a short half-life; and (d) reduction of the number of daily doses, which may increase patient adherence to the treatment. These advantages occur due to the physical, chemical and optical properties of these materials. Therefore, we discuss the properties and characteristics of them and we present some applications, using different approaches of DDS to ensure therapeutic effectiveness and side effects reduction such as implantable biomaterial, film-forming materials, stimuli-responsive systems and others.
Keywords: drug delivery systems; organic-inorganic materials; sol-gel process.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

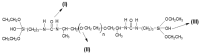
References
-
- Peppas N.A., Hilt J.Z., Khademhosseini A., Langer R. Hydrogels in biology and medicine: From molecular principles to bionanotechnology. Adv. Mater. 2006;18:1345–1360. doi: 10.1002/adma.200501612. - DOI
-
- Lin Z., Gao W., Hu H., Ma K., He B., Dai W., Wang X., Wang J., Zhang X., Zhang Q. Novel thermo-sensitive hydrogel system with paclitaxel nanocrystals: High drug-loading, sustained drug release and extended local retention guaranteeing better efficacy and lower toxicity. J. Control Release. 2014;174:161–170. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.10.026. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

