Sperm physiology varies according to ultradian and infradian rhythms
- PMID: 30979936
- PMCID: PMC6461627
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-42430-4
Sperm physiology varies according to ultradian and infradian rhythms
Abstract
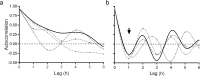
The spermatozoon must be physiologically prepared to fertilize the egg, process called capacitation. Human sperm samples are heterogeneous in their ability to capacitate themselves, which leads to variability between samples from the same or different donors, and even along the seasons. Here we studied sperm variation in the capacitation state according to the ability of capacitated spermatozoa to acrosome react upon stimulation (% ARi) and to be recruited by chemotaxis (% Chex). Both indirect indicators of sperm capacitation increased along the incubation time with fluctuations. Those capacitated sperm recruited by chemotaxis showed an ultradian rhythm with a cycle every 2 h, which might be influenced by unknown intrinsic sperm factors. Two infradian rhythms of 12 months for the % ARi and of 6 months for % Chex were observed, which are associated with the joint action of temperature and photoperiod. Thus, to avoid false negative results, human sperm samples are recommended to be incubated for a long period (e.g. 18 h) preferably in spring time. This innovative point of view would lead to better comprehend human reproductive biology and to think experimental designs in the light of sperm cyclicity or to improve sperm aptitude for clinical purposes.
Conflict of interest statement
A.M-I., J.M.K., E.M.D., A.M.V., M.N.G., R.M., C.L.T., M.J.F., A.B., N.A.P. and C.A.N.M. declare not competing interests. L.C.G. and H.A.G. are inventors of the SSA device, and the Consejo de Investigaciones Científicas y Ténicas and the Universidad Nacional de Córdoba are the owners of the patent.
Figures






References
-
- Austin, C. Observations on the Penetration of the Sperm into the Mammalian Egg. Australian journal of scientific research. Ser. B: Biological sciences4 (1951). - PubMed
-
- Zeng Y, Oberdorf JA, Florman HM. pH Regulation in Mouse Sperm: Identification of Na+-, Cl−-, and [formula] Dependent and Arylaminobenzoate-Dependent Regulatory Mechanisms and Characterization of Their Roles in Sperm Capacitation. Dev. Biol. 1996;173:510–520. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1996.0044. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

