Esophagogastric Junction Outflow Obstruction Caused by Gabapentin
- PMID: 30982245
- PMCID: PMC6474712
- DOI: 10.5056/jnm19004
Esophagogastric Junction Outflow Obstruction Caused by Gabapentin
Conflict of interest statement
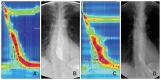
Figures
References
-
- Boeckxstaens GE, Beaumont H, Hatlebakk JG, et al. A novel reflux inhibitor lesogaberan (AZD3355) as add-on treatment in patients with GORD with persistent reflux symptoms despite proton pump inhibitor therapy: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Gut. 2011;60:1182–1188. doi: 10.1136/gut.2010.235630. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

