Cost-Effectiveness of the US Food and Drug Administration Added Sugar Labeling Policy for Improving Diet and Health
- PMID: 30982338
- PMCID: PMC6546520
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.036751
Cost-Effectiveness of the US Food and Drug Administration Added Sugar Labeling Policy for Improving Diet and Health
Abstract
Background: Excess added sugars, particularly from sugar-sweetened beverages, are a major risk factor for cardiometabolic diseases including cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus. In 2016, the US Food and Drug Administration mandated the labeling of added sugar content on all packaged foods and beverages. Yet, the potential health impacts and cost-effectiveness of this policy remain unclear.
Methods: A validated microsimulation model (US IMPACT Food Policy model) was used to estimate cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus cases averted, quality-adjusted life-years, policy costs, health care, informal care, and lost productivity (health-related) savings and cost-effectiveness of 2 policy scenarios: (1) implementation of the US Food and Drug Administration added sugar labeling policy (sugar label), and (2) further accounting for corresponding industry reformulation (sugar label+reformulation). The model used nationally representative demographic and dietary intake data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, disease data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Wonder Database, policy effects and diet-disease effects from meta-analyses, and policy and health-related costs from established sources. Probabilistic sensitivity analysis accounted for model parameter uncertainties and population heterogeneity.
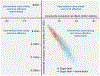
Results: Between 2018 and 2037, the sugar label would prevent 354 400 cardiovascular disease (95% uncertainty interval, 167 000-673 500) and 599 300 (302 400-957 400) diabetes mellitus cases, gain 727 000 (401 300-1 138 000) quality-adjusted life-years, and save $31 billion (15.7-54.5) in net healthcare costs or $61.9 billion (33.1-103.3) societal costs (incorporating reduced lost productivity and informal care costs). For the sugar label+reformulation scenario, corresponding gains were 708 800 (369 200-1 252 000) cardiovascular disease cases, 1.2 million (0.7-1.7) diabetes mellitus cases, 1.3 million (0.8-1.9) quality-adjusted life-years, and $57.6 billion (31.9-92.4) and $113.2 billion (67.3-175.2), respectively. Both scenarios were estimated with >80% probability to be cost saving by 2023.
Conclusions: Implementing the US Food and Drug Administration added sugar labeling policy could generate substantial health gains and cost savings for the US population.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; cost-benefit analysis; diabetes mellitus; diet; food labeling; policy; prevention & control.
Figures



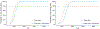
Comment in
-
Added Sugar Labeling.Circulation. 2019 Jun 4;139(23):2625-2627. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.040325. Epub 2019 Jun 3. Circulation. 2019. PMID: 31157997 No abstract available.
References
-
- Food and Drug Administration. Food labeling: revision of the Nutrition and Supplement Facts Labels; final rule. 2016;21 CFR 101. Federal Register 2016;103: 33742–33999. - PubMed
-
- Te Morenga L, Mallard S and Mann J. Dietary sugars and body weight: systematic review and meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials and cohort studies. BMJ. 2013;346:e7492–e7492. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

