Summary of Workshop Large Outdoor Fires and the Built Environment
- PMID: 30983689
- PMCID: PMC6459202
- DOI: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2018.07.002
Summary of Workshop Large Outdoor Fires and the Built Environment
Abstract
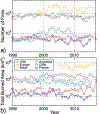
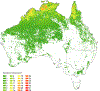
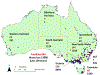
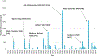
Large outdoor fires present a risk to the built environment. Wildfires that spread into communities, referred to as Wildland-Urban Interface (WUI) fires, have destroyed communities throughout the world, and are an emerging problem in fire safety science. Other examples are large urban fires including those that have occurred after earthquakes. Research into large outdoor fires, and how to potentially mitigate the loss of structures in such fires, lags other areas of fire safety science research. At the same time, common characteristics between fire spread in WUI fires and urban fires have not been fully exploited. In this paper, an overview of the large outdoor fire risk to the built environment from each region is presented. Critical research needs for this problem in the context offire safety science are provided. The present paper seeks to develop the foundation for an international research needs roadmap to reduce the risk of large outdoor fires to the built environment.
Figures

References
-
- 2007 Annual Report of the Insurance Commissioner, California Department of Insurance.
-
- 2009 Victorian Bushfires Royal Commission, Final Summary Report, July 2010.
-
- Gorte R., The Rising Costs of Wildfire Protection, Headwaters Economics, June, 2013.
-
- Manzello SL (2014) Enabling the Investigation of Structure Vulnerabilities to Wind-Driven Firebrand Showers in Wildland Urban Interface (WUI) Fires, Fire Safety Science 11: 83–96, 10.3801/IAFSS.FSS.11-83. - DOI
