Nox2-dependent Neuroinflammation in An EAE Model of Multiple Sclerosis
- PMID: 30984416
- PMCID: PMC6455010
- DOI: 10.1515/tnsci-2019-0001
Nox2-dependent Neuroinflammation in An EAE Model of Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
Background: Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an inflammatory disease of the CNS, characterized by demyelination, focal inflammatory infiltrates and axonal damage. Oxidative stress has been linked to MS pathology. Previous studies have suggested the involvement of NADPH oxidase 2 (Nox2), an enzyme that catalyzes the reduction of oxygen to produce reactive oxygen species, in the MS pathogenesis. The mechanisms of Nox2 activation on MS are unknown. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of Nox2 deletion on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) onset and severity, on astrocyte activation as well as on pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine induction in striatum and motor cortex.
Methodology: Subcutaneous injection of MOG35-55 emulsified with complete Freund's adjuvant was used to evaluate the effect of Nox2 depletion on EAE-induced encephalopathy. Striatum and motor cortices were isolated and evaluated by immunoblotting and RT-PCR.
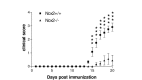
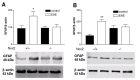
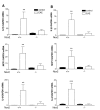
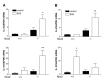
Results: Nox2 deletion resulted in clinical improvement of the disease and prevented astrocyte activation following EAE induction. Nox2 deletion prevented EAE-induced induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines and stimulated the expression of the anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-4 and IL-10.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that Nox2 is involved on the EAE pathogenesis. IL-4 and IL-10 are likely to be involved on the protective mechanism observed following Nox2 deletion.
Keywords: Multiple sclerosist; NADPH oxidaset; astrocytest; cytokines.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The author has no conflicts of interest related to this work.
Figures

References
-
- Geurts JJ, Barkhof F. Grey matter pathology in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7(9):841–51. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
