Investigation of Circulating Serum MicroRNA-328-3p and MicroRNA-3135a Expression as Promising Novel Biomarkers for Autism Spectrum Disorder
- PMID: 30984518
- PMCID: PMC6454235
- DOI: 10.2478/bjmg-2018-0026
Investigation of Circulating Serum MicroRNA-328-3p and MicroRNA-3135a Expression as Promising Novel Biomarkers for Autism Spectrum Disorder
Abstract
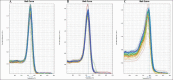
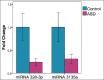
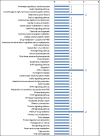
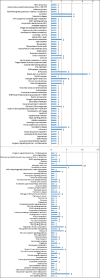
Circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) are emerging as promising diagnostic biomarkers for autism spectrum disorder (ASD), but their usefulness for detecting ASD remains unclear. Nowadays, development of promising biomarkers for ASD remains a challenge. Recently, dysregulation of the miRNAs expression in postmortem brain tissue, serum and peripheral blood, have been associated with ASD. Circulating miRNAs are known to be secreted by a number of different cells and can interpose delivery of information into receiver cells, thus affecting their functions. Based on this fact, it is supposed that serum miRNAs could be a novel class of biomarkers for prognosis or diagnosis of pathological disorders including ASD. In the current research, we investigated whether the expression patterns of circulating miRNAs showed dysregulation in subjects diagnosed with ASD. Expression levels of serum miR-328-3p and miR-3135a were analyzed by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) method of subjects diagnosed with ASD in comparison with healthy control subjects. Our data showed that miR-328-3p and miR-3135a were substantially down-regulated in ASD patients than in those of healthy control subjects. Moreover, target gene analysis of altered serum miRNAs displayed that these molecules targeted 162 genes denoted as unique validated targets in the miRWalk database, 71 of which appear to participate in biological pathways involved in synaptic pathways and neurodegenerative condition such as Alzheimer, Huntington and Parkinson diseases. Finally, the results strongly suggested that dys-regulated serum miRNAs might be involved in molecular pathways associated with ASD and miR-328-3p and miR-3135a have the potential to be promising novel biomarkers for ASD.
Keywords: Autism spectrum disorder (ASD); MicroRNA (miRNA) expression profiling; Serum miRNAs; Stem-loop quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR).
Figures


References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell. 2004;116(2):281–297. - PubMed
-
- Mattick JS, Makunin IV. Non-coding RNA. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15(15):R17–R29. - PubMed
-
- Fombonne E. Epidemiology of pervasive developmental disorders. Pediatr Res. 2009;65(6):591–598. - PubMed
-
- Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network Surveillance Year. Principal Investigators, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years– autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2010. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2010;2014;63(2):1–21. - PubMed
-
- Rutter M. Incidence of autism spectrum disorders: Changes over time and their meaning. Acta Paediatr. 2005;94(1):2–15. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
