Preanalytical sample handling recommendations for Alzheimer's disease plasma biomarkers
- PMID: 30984815
- PMCID: PMC6446057
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dadm.2019.02.002
Preanalytical sample handling recommendations for Alzheimer's disease plasma biomarkers
Abstract
Introduction: We examined the influence of common preanalytical factors on the measurement of Alzheimer's disease-specific biomarkers in human plasma.
Methods: Amyloid β peptides (Aβ[1-40], Aβ[1-42]) and total Tau plasma concentrations were quantified using fully automated Roche Elecsys assays.
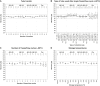
Results: Aβ(1-40), Aβ(1-42), and total Tau plasma concentrations were not affected by up to three freeze/thaw cycles, up to five tube transfers, the collection tube material, or the size; circadian rhythm had a minor effect. All three biomarkers were influenced by the anticoagulant used, particularly total Tau. Aβ concentrations began decreasing 1 hour after blood draw/before centrifugation and decreased by up to 5% and 10% at 2 and 6 hours, respectively. For separated plasma, time to measurement influenced Aβ levels by up to 7% after 6 hours and 10% after 24 hours.
Discussion: Our findings provide guidance for standardizing blood sample collection, handling, and storage to ensure reliable analysis of Alzheimer's disease plasma biomarkers in routine practice and clinical trials.
Keywords: AD; Alzheimer's disease; Alzheimer's disease-specific biomarkers; Amyloid; Biomarkers; Elecsys immunoassay; Fully automated; Plasma; Preanalytics; Sample handling; Tau.
Figures


References
-
- Waldemar G., Phung K.T., Burns A., Georges J., Hansen F.R., Iliffe S. Access to diagnostic evaluation and treatment for dementia in Europe. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2007;22:47–54. - PubMed
-
- Simonsen A.H., Herukka S.K., Andreasen N., Baldeiras I., Bjerke M., Blennow K. Recommendations for CSF AD biomarkers in the diagnostic evaluation of dementia. Alzheimers Dement. 2017;13:274–284. - PubMed
-
- Blennow K., Zetterberg H. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2009;18:413–417. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
