Two episodes of remote ischemia preconditioning improve motor and sensory function of hind limbs after spinal cord ischemic injury
- PMID: 30985269
- PMCID: PMC7801032
- DOI: 10.1080/10790268.2019.1600829
Two episodes of remote ischemia preconditioning improve motor and sensory function of hind limbs after spinal cord ischemic injury
Abstract
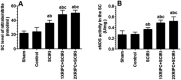
Objectives: To investigate the effect of one and two remote ischemia preconditioning episodes (1-RIPC or 2-RIPC, respectively) on neuro-protection after spinal cord ischemic injury (SCI) in rats. Design: Experimental animal study. Setting: College of Medicine, King Khalid University, Abha, KSA. Interventions: Male rats (n = 10/group) were divided into control, sham, SCIRI, 1-RIPC + SCIRI, and 2-RIPC + SCIRI. SCI was induced by aortic ligation for 45 min and each RIPC episode was induced by 3 cycles of 10 min ischemia/10 min perfusion. The two preconditioning procedures were separated by 24 h. Outcome measures: after 48 h of RIPC procedure, Tarlov's test, withdrawal from the painful stimulus and placing/stepping reflex (SPR) were used to evaluate the hind limbs neurological function. SC homogenates were used to measure various biochemical parameters. Results: Motor and sensory function of hind limbs were significantly improved and levels of MDA, AOPPs, PGE2, TNF-α, and IL-6, as well as the activity of SOD, was significantly decreased in SC tissue in either 1 or 2 episodes of RIPC intervention. Concomitantly, levels of total nitrate/nitrite and eNOS activity were significantly increased in both groups. Interestingly, except for activity of SOD, eNOS and levels of nitrate/nitrite, the improvements in all neurological biochemical endpoint were more profound in 2-RIPC + SCIRI compared with 1-RIPC + SCIRI. Conclusion: applying two preconditioning episodes of 3 cycles of 10 min ischemia/10 min perfusion, separated by 24 h, boost the neuro-protection effect of RIPC maneuver in rats after ischemic induced SCI in rats.
Keywords: Aorta; Delayed; Protection; Remote ischemic preconditioning; Spinal cord.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Protective Effect of Contralateral, Ipsilateral, and Bilateral Remote Ischemic Preconditioning on Spinal Cord Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in Rats.Turk Neurosurg. 2019;29(6):933-939. doi: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.26237-19.3. Turk Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 31608967
-
Effects of ischemic preconditioning protocols on skeletal muscle ischemia-reperfusion injury.J Surg Res. 2015 Feb;193(2):942-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2014.09.032. Epub 2014 Sep 30. J Surg Res. 2015. PMID: 25438960
-
Comparison of the protective effects of direct ischemic preconditioning and remote ischemic preconditioning in a rabbit model of transient spinal cord ischemia.J Anesth. 2018 Feb;32(1):3-14. doi: 10.1007/s00540-017-2420-5. Epub 2017 Nov 1. J Anesth. 2018. PMID: 29094209
-
Remote ischemic preconditioning: a novel protective method from ischemia reperfusion injury--a review.J Surg Res. 2008 Dec;150(2):304-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2007.12.747. Epub 2008 Jan 22. J Surg Res. 2008. PMID: 19040966 Review.
-
Advance in spinal cord ischemia reperfusion injury: Blood-spinal cord barrier and remote ischemic preconditioning.Life Sci. 2016 Jun 1;154:34-8. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.03.046. Epub 2016 Apr 7. Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27060223 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the sigma-1 receptor with pridopidine induces functional neurorestoration in spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul;398(7):9307-9321. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03851-3. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39937253 Free PMC article.
-
Remote ischemic preconditioning protects against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice by activating NMDAR/AMPK/PGC-1α/SIRT3 signaling.Cell Biosci. 2023 Mar 16;13(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-00999-4. Cell Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36927808 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in organ protection: ischemic preconditioning and erythropoietin as protective strategies.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Jun 2. doi: 10.1007/s11255-025-04586-z. Online ahead of print. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40455321 Review.
References
-
- Toumpoulis IK, Anagnostopoulos CE, Drossos GE, Malamou-Mitsi VD, Pappa LS, Katritsis DG.. Does ischemic preconditioning reduce spinal cord injury because of descending thoracic aortic occlusion? J Vasc Surg. 2003;37(2):426–32. - PubMed
-
- Coselli JS, LeMaire SA, Conklin LD, Koksoy C, Schmittling ZC.. Morbidity and mortality after extent II thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Ann Thorac Surg. 2002;73(4):1107–16. - PubMed
-
- Svensson LG, Crawford ES, Hess KR, Coselli JS, Safi HJ.. Experience with 1509 patients undergoing thoracoabdominal aortic operations. J Vasc Surg. 1993;17(2):357–68. - PubMed
-
- Estrera AL, Miller CC III, Huynh TT, Porat E, Safi HJ.. Neurologic outcome after thoracic and thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001;72:1225–30. - PubMed
-
- Isbir CS, Ak K, Kurtkaya O, Zeybek U, Akgün S, Scheitauer BW, et al. . Ischemic preconditioning and nicotinamide in spinal cord protection in an experimental model of transient aortic occlusion. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2003;23(6):1028–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
