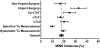Myocardial Injury After Noncardiac Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 30985328
- PMCID: PMC6776733
- DOI: 10.1097/CRD.0000000000000254
Myocardial Injury After Noncardiac Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
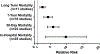
Myocardial injury after noncardiac surgery (MINS) is a common postoperative complication associated with adverse cardiovascular outcomes. The purpose of this systematic review was to determine the incidence, clinical features, pathogenesis, management, and outcomes of MINS. We searched PubMed, Embase, Central and Web of Science databases for studies reporting the incidence, clinical features, and prognosis of MINS. Data analysis was performed with a mixed-methods approach, with quantitative analysis of meta-analytic methods for incidence, management, and outcomes, and a qualitative synthesis of the literature to determine associated preoperative factors and MINS pathogenesis. A total of 195 studies met study inclusion criteria. Among 169 studies reporting outcomes of 530,867 surgeries, the pooled incidence of MINS was 17.9% [95% confidence interval (CI), 16.2-19.6%]. Patients with MINS were older, more frequently men, and more likely to have cardiovascular risk factors and known coronary artery disease. Postoperative mortality was higher among patients with MINS than those without MINS, both in-hospital (8.1%, 95% CI, 4.4-12.7% vs 0.4%, 95% CI, 0.2-0.7%; relative risk 8.3, 95% CI, 4.2-16.6, P < 0.001) and at 1-year after surgery (20.6%, 95% CI, 15.9-25.7% vs 5.1%, 95% CI, 3.2-7.4%; relative risk 4.1, 95% CI, 3.0-5.6, P < 0.001). Few studies reported mechanisms of MINS or the medical treatment provided. In conclusion, MINS occurs frequently in clinical practice, is most common in patients with cardiovascular disease and its risk factors, and is associated with increased short- and long-term mortality. Additional investigation is needed to define strategies to prevent MINS and treat patients with this diagnosis.
Figures
References
-
- Weiser TG, Haynes AB, Molina G, et al. Estimate of the global volume of surgery in 2012: An assessment supporting improved health outcomes. Lancet. 2015;385 Suppl 2:S11 - PubMed
-
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, et al. Third universal definition of myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60:1581–1598 - PubMed
-
- van Waes JA, Nathoe HM, de Graaff JC, et al. Myocardial injury after noncardiac surgery and its association with short-term mortality. Circulation. 2013;127:2264–2271 - PubMed
-
- Thygesen K, Mair J, Katus H, et al. Recommendations for the use of cardiac troponin measurement in acute cardiac care. Eur Heart J. 2010;31:2197–2204 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous