Switching to Doravirine/Lamivudine/Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate (DOR/3TC/TDF) Maintains HIV-1 Virologic Suppression Through 48 Weeks: Results of the DRIVE-SHIFT Trial
- PMID: 30985556
- PMCID: PMC6905402
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000002056
Switching to Doravirine/Lamivudine/Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate (DOR/3TC/TDF) Maintains HIV-1 Virologic Suppression Through 48 Weeks: Results of the DRIVE-SHIFT Trial
Abstract
Background: Doravirine is a novel, nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor with demonstrated efficacy in treatment-naive adults with HIV-1.
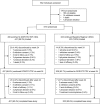
Methods: In this open-label, active-controlled, noninferiority trial, adults with HIV-1 virologically suppressed for ≥6 months on 2 nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors plus a boosted protease inhibitor, boosted elvitegravir, or a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor were randomized (2:1) to switch to once-daily, single-tablet doravirine 100 mg with lamivudine 300 mg and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate 300 mg (DOR/3TC/TDF) or to continue their current therapy (Baseline Regimen) for 24 weeks. The primary endpoint was the proportion of participants with HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL (defined by the FDA Snapshot approach), with the primary comparison between DOR/3TC/TDF at week 48 and Baseline Regimen at week 24 and a secondary comparison between the groups at week 24 (noninferiority margin, -8%).
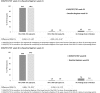
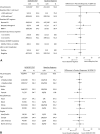
Results: Six hundred seventy participants (447 DOR/3TC/TDF, 223 Baseline Regimen) were treated and included in the analyses. At week 24, 93.7% on DOR/3TC/TDF vs 94.6% on Baseline Regimen had HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL [difference -0.9 (-4.7 to 3.0)]. At week 48, 90.8% on DOR/3TC/TDF had HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL, demonstrating noninferiority vs Baseline Regimen at week 24 [difference -3.8 (-7.9 to 0.3)]. In participants on ritonavir-boosted protease inhibitor at entry, mean reductions in fasting LDL-C and non-HDL-C at week 24 were significantly greater for DOR/3TC/TDF vs Baseline Regimen (P < 0.0001). Adverse events occurred in 68.9% on DOR/3TC/TDF and 52.5% on Baseline Regimen by week 24, leading to treatment discontinuation in 2.5% and 0.4%, respectively.
Conclusions: Switching to once-daily DOR/3TC/TDF is a generally well-tolerated option for maintaining viral suppression in patients considering a change in therapy.
Registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02397096.
Conflict of interest statement
M.J. has received grants and consulting fees from Gilead and ViiV. P.K. is on Advisory Boards for ViiV, Janssen, Merck, and Theratechnologies; has received grants from Merck, ViiV, Gilead, and Theratechnologies; and owns stock in Johnson & Johnson, Gilead, Merck, Pfizer, and GSK. J.-M.M. has received grants from Gilead and consulting fees (Advisory Board) from Gilead and MSD. G.R. has received Advisory board and speaker fees from Janssen-Cilag, Abbvie, Gilead Science, ViiV, MSD, and Angelini. P.C. is an Advisory Board member for MSD and ViiV and has received research grants from AbbVie, MSD, and ViiV. J.M. has received honoraria, speakers' fees, consultant fees or funds for research from MSD, Roche, Boehringer-Ingelheim, ViiV, Gilead, Janssen, BMS, and Abbvie. Y.Z., C.M., S.K., P.S., G.J.H., C.H., and W.G. are current or former employees of MSD. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Beyrer C, Pozniak A. HIV drug resistance—an emerging threat to epidemic control. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:1605–1607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

